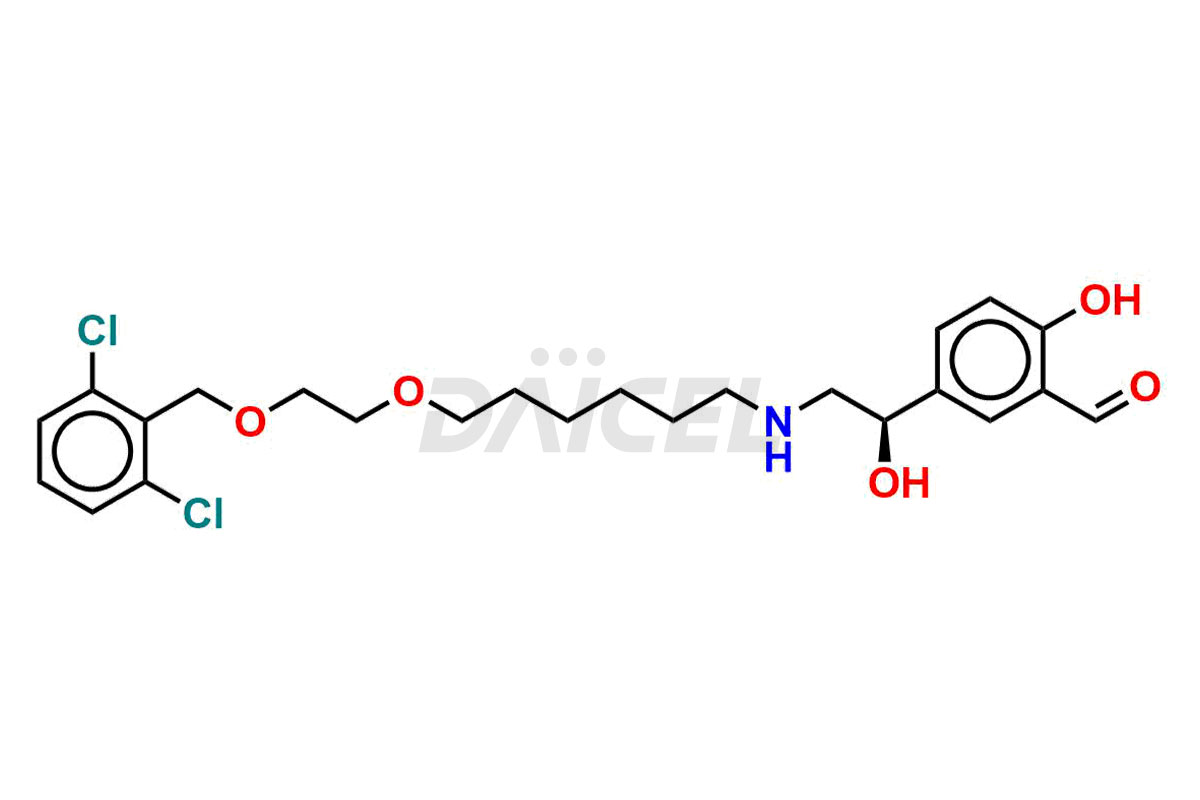
Vilanterol
General Information
Vilanterol Impurities and Vilanterol
Daicel Pharma synthesizes high-quality Vilanterol impurities, such as S-Vilanterol, Vilanterol Impurity -29, Vilanterol Impurity -28, Vilanterol Dimer impurity, Vilanterol Impurity – 1, S-Vilanterol trifenatate, and VLT Aldehyde Impurity, crucial in analyzing the quality, stability, and biological safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient, Vilanterol. Moreover, Daicel Pharma offers custom synthesis of Vilanterol impurities and delivers them globally.
Vilanterol [CAS: 503068-34-6] is a dichlorobenzene derivative, available as its trifenate salt, to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). As a beta2-adrenergic agonist and bronchodilator agent, Vilanterol helps to alleviate symptoms associated with this respiratory condition.
Vilanterol: Use and Commercial Availability
Vilanterol is utilized in combination with other drugs in several FDA-approved products like Breo Ellipta, Anoro Ellipta, and Trelegy Ellipta. Breo Ellipta was approved in 2013 to treat airflow obstruction in patients with COPD, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. Also, to treat asthma in patients aged 18 years or older with reversible obstructive airway disease. Anoro Ellipta is used to maintain the treatment of patients with COPD, and Trelegy Ellipta is used treat patients with COPD and asthma in patients aged 18 years and older. Vilanterol is an active component of these drugs.
Vilanterol Structure and Mechanism of Action 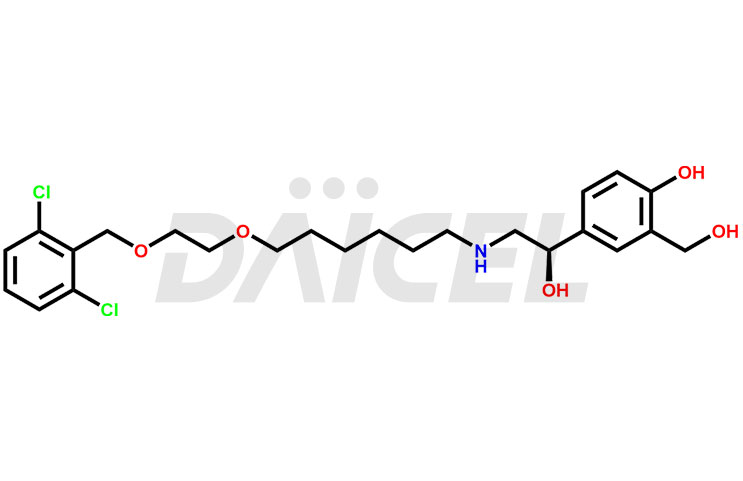
The chemical name of Vilanterol is 4-[(R)-2-[[6-[2-(2,6-Dichlorobenzyloxy)ethoxy]hexyl]amino]-1-hydroxyethyl]-2-hydroxymethyl phenol. Its chemical formula for Vilanterol is C24H33Cl2NO5 and its molecular weight is approximately 486.4 g/mol.
Vilanterol is a type of ultra-long-acting beta2-adrenoceptor agonist that works by binding to the β2-adrenergic receptor to regulate the relaxation or dilation of the bronchial smooth muscle. As a result, it provides relief from the symptoms of bronchospasm that are commonly associated with asthma and COPD.
Vilanterol Impurities and Synthesis
Vilanterol impurities fall into three categories: process impurities, degradation impurities, and potentially genotoxic impurities (PGIs). Process impurities that occur during production1 consist of solvents, reagents, and by-products. Degradation impurities produced during the handling or storage of the drug substance or product, and they may include oxidation, hydrolysis, and photodegradation products. PGIs are impurities that have the potential to cause genetic mutations and are strictly regulated. The formation of Vilanterol impurities is influenced by various factors, such as temperature, humidity, and pH. It is essential to closely monitor and control the levels of these impurities in Vilanterol to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the medication.
Daicel offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from a cGMP-compliant analytical facility for Vilanterol impurity standards, including S-Vilanterol, Vilanterol Impurity -29, Vilanterol Impurity -28, Vilanterol Dimer impurity, Vilanterol Impurity – 1, S-Vilanterol trifenatate, and VLT Aldehyde Impurity. The CoA includes complete characterization data, such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity2. We also provide 13C-DEPT and CHN on request. We also give a complete characterization report on delivery.
Daicel has the technology and expertise to prepare any unknown Vilanterol impurity or degradation product. We also provide labeled compounds to quantify the efficacy of generic Vilanterol. Daicel offers highly pure isotope-labeled standards of Vilanterol for bioanalytical research and BA/BE studies.
References
FAQ's
References
- Box, Philip Charles; Coe, Diane Mary; Looker, Brian Edgar; Procopiou, Panayiotis Alexandrou, “Phenethanolamine Derivatives For Treatment Of Respiratory Diseases”, Glaxo Group Limited, United Kingdom, EP1425001B1, September 11, 2002.
- Goergens, Christian; Guddat, Sven; Thomas, Andreas; Wachsmuth, Philipp; Orlovius, Anne-Katrin; Sigmund, Gerd; Thevis, Mario; Schaenzer, Wilhelm, “Simplifying and expanding analytical capabilities for various classes of doping agents by means of direct urine injection high performance liquid chromatography high resolution/high accuracy mass spectrometry”, Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, Volume: 131, Pages: 482-496, 2016
Frequently Asked Questions
How are Vilanterol impurities identified?
Vilanterol impurities can be identified using various analytical techniques such as High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS), etc.
How are impurities removed from Vilanterol?
Vilanterol impurities can be removed from the drug using various techniques such as chromatography, recrystallization, and solvent extraction.
What chromatography techniques are used in the purification of Vilanterol impurities?
Preparative HPLC, Flash Chromatography, and TLC are chromatographic techniques used for the purification of Vilanterol impurities. These techniques separate the impurities from Vilanterol and help in the drug’s purification.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Vilanterol impurities?
Vilanterol impurities should be stored at a controlled room temperature of between 2-8 ⁰C.
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.