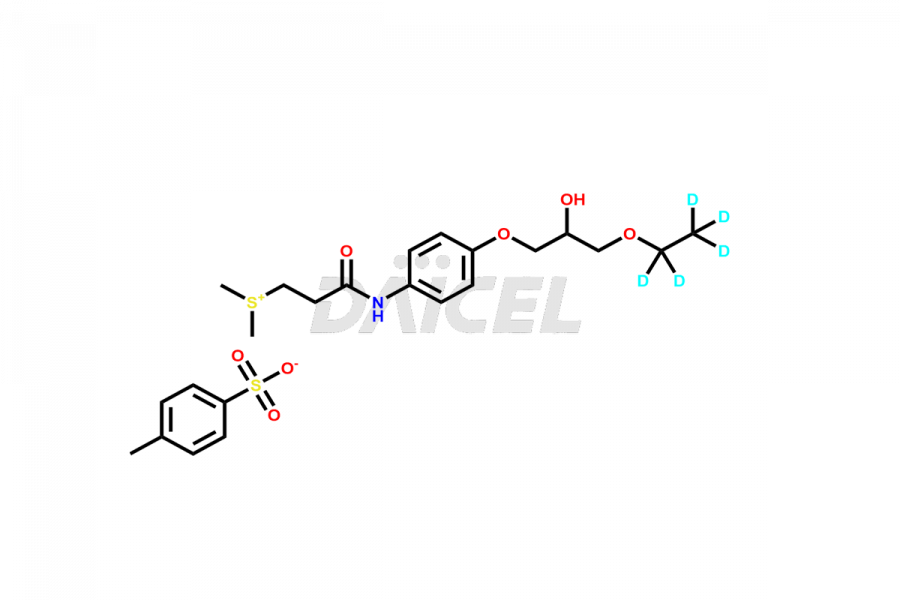
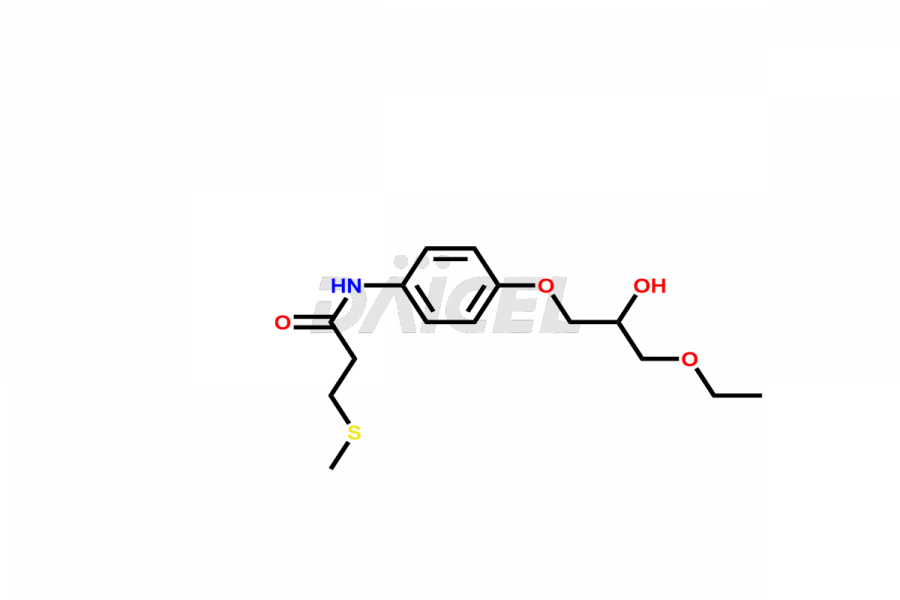
Suplatast
General Information
Suplatast Impurities and Suplatast
Daicel Pharma offers Suplatast impurities like 1-(4-aminophenoxy)-3-ethoxypropane-2-ol, N-(4-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxypropoxy), phenyl)-3-(methylthio)propanamide, N-(4-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxypropoxy)phenyl), acrylamide and N-(4-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxypropoxy)phenyl)-3-hydroxypropanamide, etc. The impurities are of utmost importance when assessing the quality, stability, and biological safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient Suplatast. Daicel Pharma specializes in synthesizing custom Suplatast impurities to meet precise customer specifications. With a commitment to worldwide delivery, Daicel Pharma ensures that customers receive the synthesized Suplatast impurities promptly and reliably.
Suplatast [CAS: 94055-75-1] is a medicine primarily used to treat allergic diseases, including asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis. It is classified as an immunomodulator and suppresses the immune response associated with allergic reactions.
Suplatast: Use and Commercial Availability
Suplatast, an innovative immunomodulator, can restore the equilibrium in the Th1/Th2 immune response and demonstrates notable clinical effectiveness in managing bronchial asthma (BA). Suplatast treats BA, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis.
Suplatast is available under Tosilart, IPD-1151T, etc., which contains the active ingredient, Suplatast.
Suplatast Structure and Mechanism of Action 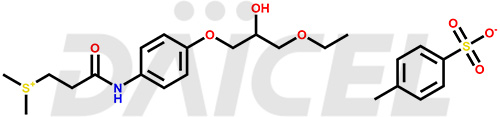
The chemical name of Suplatast is [3-[[4-(3-Ethoxy-2-hydroxypropoxy)phenyl]amino]-3-oxopropyl]dimethylsulfonium. Its chemical formula is C16H26NO4S, and its molecular weight is approximately 328.4 g/mol.
Suplatast inhibits the production of IgE, impeding cytokine production and suppressing eosinophils associated with allergies.
Suplatast Impurities and Synthesis
During the synthesis and storage of Suplatast1, impurities can arise, including related substances, degradation products, and residual solvents. It is essential to carefully monitor and control these impurities to ensure the medication’s safety, efficacy, and overall quality.
Daicel Pharma offers a comprehensive Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for impurity standards such as – 1-(4-aminophenoxy)-3-ethoxypropane-2-ol, N-(4-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxypropoxy), phenyl)-3-(methylthio)propanamide, N-(4-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxypropoxy)phenyl), acrylamide and N-(4-(3-ethoxy-2-hydroxypropoxy)phenyl)-3-hydroxy propenamide, etc. These impurities form in compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). The CoA includes detailed characterization data, such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity, providing a thorough understanding of the impurity profile. Upon request, Daicel can also provide 13C-DEPT data for further characterization.
Furthermore, Daicel Pharma possesses the technical expertise to synthesize any unknown impurities or degradation products of Suplatast. Daicel Pharma also provides labeled compounds specifically designed to assess the effectiveness of generic versions of Suplatast. Daicel Pharma offers highly pure Deuterated Suplatast Tosilate, the deuterated-labeled standard of Suplatast for bioanalytical research and Bioavailability/Bioequivalence (BA/BE) studies.
References
FAQ's
Frequently Asked Questions
How are Suplatast impurities detected and quantified?
Analytical Methods such as Reverse Phase-High Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC) can detect impurities in Suplatast.
Can Suplatast impurities affect patient safety?
Suplatast impurities can impact patient safety. Depending on their nature and concentration, contaminants can cause adverse effects or reduce the efficacy of the medication.
Which solvents help in the analysis of Suplatast impurities?
Acetonitrile is used to achieve optimal solubility and separation of Suplatast impurities.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Suplatast impurities?
Suplatast impurities are stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8 ⁰C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.