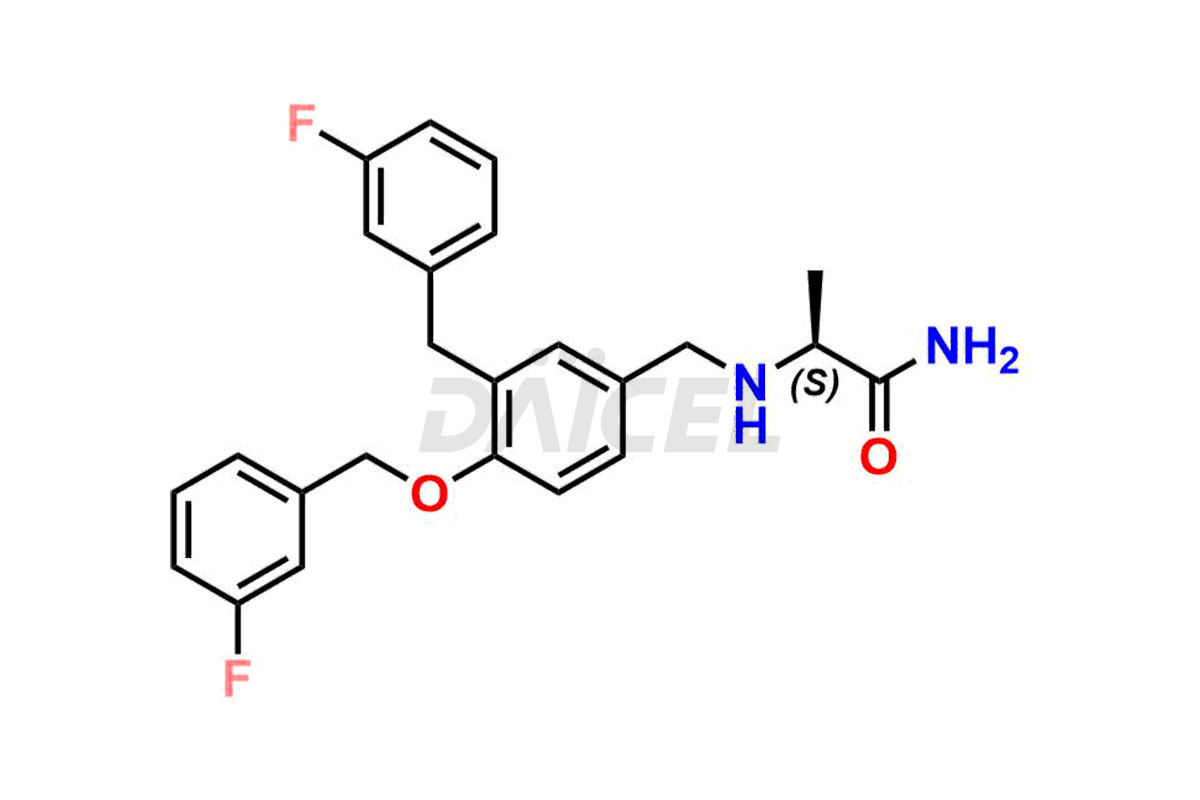
Safinamide
General Information
Safinamide Impurities and Safinamide
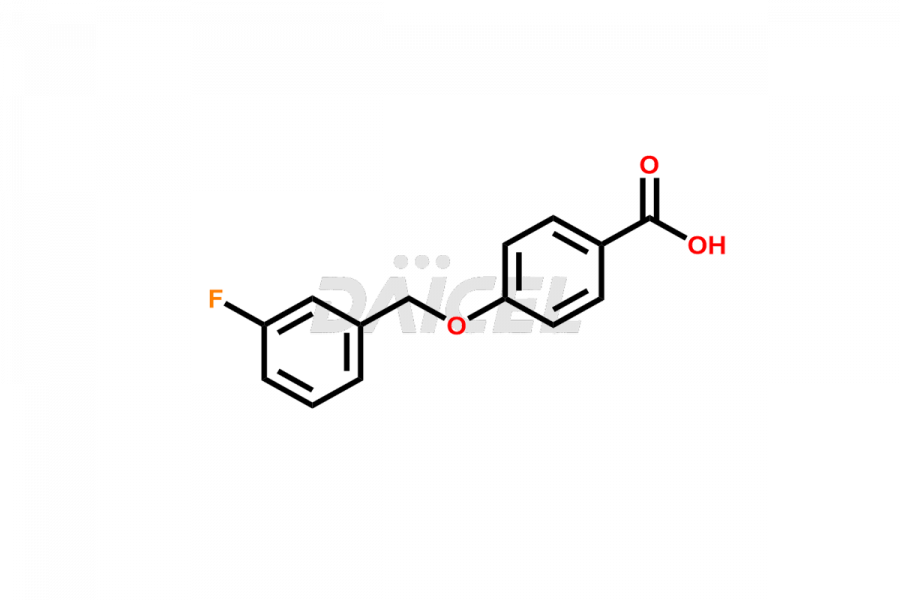
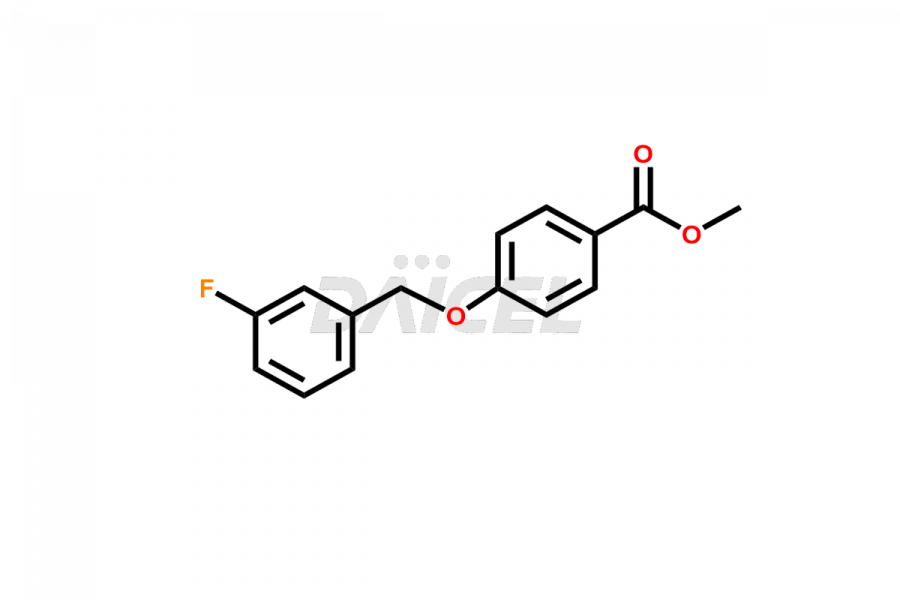
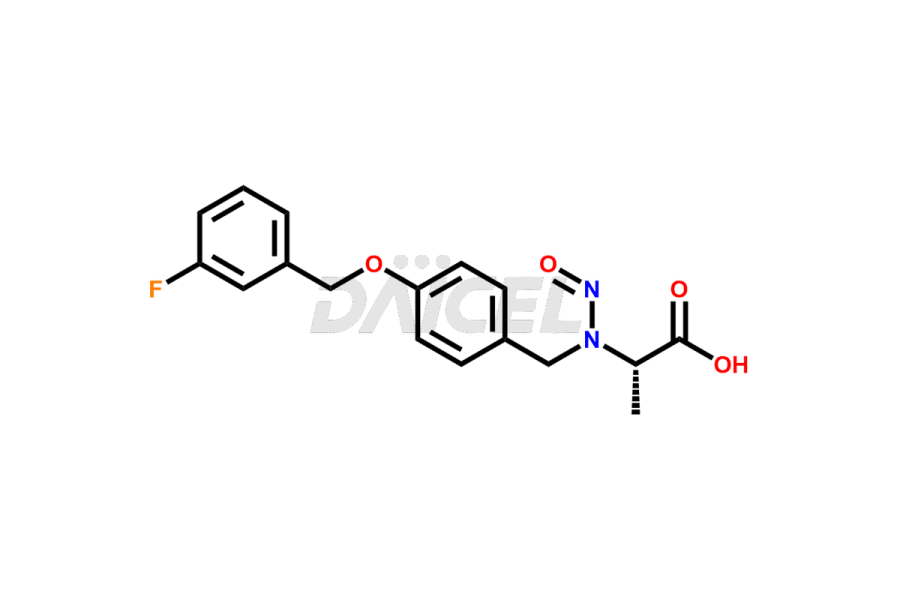
Daicel Pharma offers optimal Safinamide impurities such as Safinamide Amide Impurity, 4-((3-fluorobenzyl)oxy)benzaldehyde, 4-((3-fluorobenzyl)oxy)benzoic acid, and Safinamide N-Oxide among many others. The active pharmaceutical ingredient Safinamide’s quality, stability, and biological safety depend on these impurities. Daicel Pharma can also synthesize Safinamide impurities according to the customers’ specific needs and deliver them worldwide.
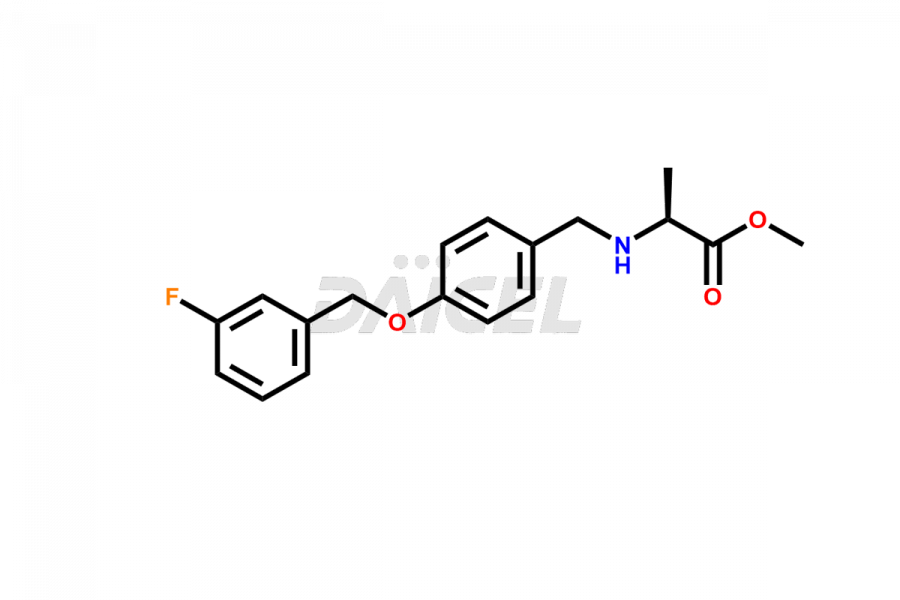
Safinamide [CAS: 133865-89-1] is an orally active, selective, reversible monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor that treats mid-to-late fluctuating Parkinson’s disease combined with levodopa/carbidopa medications for Parkinson’s disease.
Safinamide: Use and Commercial Availability
Safinamide is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor used as an adjunctive therapy alongside levodopa and carbidopa for treating Parkinson’s disease. By inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase-B, Safinamide helps stabilize motor fluctuations. It also improves specific non-motor symptoms and can significantly enhance the quality of life for patients. This medicine is available under Xadago, which effectively contains the active ingredient – Safinamide.
Safinamide Structure and Mechanism of Action 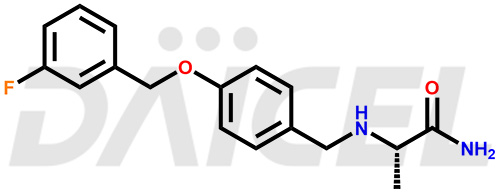
The chemical name of Safinamide is (2S)-2-[[[4-[(3-Fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]methyl]amino]propenamide. Its chemical formula is C17H19FN2O2, and its molecular weight is approximately 302.34 g/mol.
Safinamide inhibits monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B), leading to increased dopamine activity in the brain. However, the exact mechanism of Safinamide is unknown.
Safinamide Impurities and Synthesis
Safinamide impurities form during synthesis1 and vary depending on the synthetic route and the reaction conditions. Vigilant monitoring and regulation of impurity formation are essential, as these impurities can affect the drug’s efficacy.
Daicel offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from a cGMP-compliant analytical facility for Safinamide impurity standards like Safinamide Amide Impurity, 4-((3-fluorobenzyl)oxy)benzaldehyde, 4-((3-fluorobenzyl)oxy)benzoic acid and Safinamide N-Oxide among many others. The CoA includes complete characterization data, such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity2. We provide additional characterization data, including 13C-DEPT, upon request. Daicel Pharma generates unknown impurities or degradation products of Safinamide.
References
FAQ's
References
Frequently Asked Questions
How are Safinamide impurities detected and quantified?
Analytical methods, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), are commonly used to detect and quantify impurities in Safinamide. The most effective separation of impurities involved using an Inertsil ODS-3 column with a mobile phase consisting of 0.1% formic acid in water (pH adjusted to 5.0) and acetonitrile in gradient mode.
Can Safinamide impurities affect patient safety?
Yes, impurities in safinamide can impact patient safety. Depending on their nature and concentration, contaminants can cause adverse effects or reduce the efficacy of the medication.
Why is it essential to synthesize Safinamide impurities?
It is essential to synthesize impurities of Safinamide to accurately identify, characterize, and establish their permissible limits within the drug product.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Safinamide impurities?
Safinamide impurities should be stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8 ⁰C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.