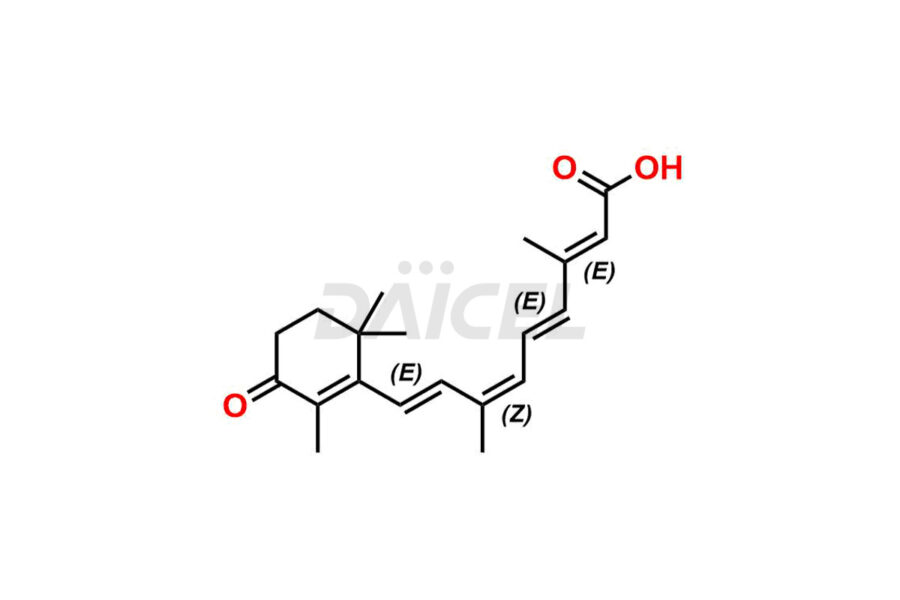
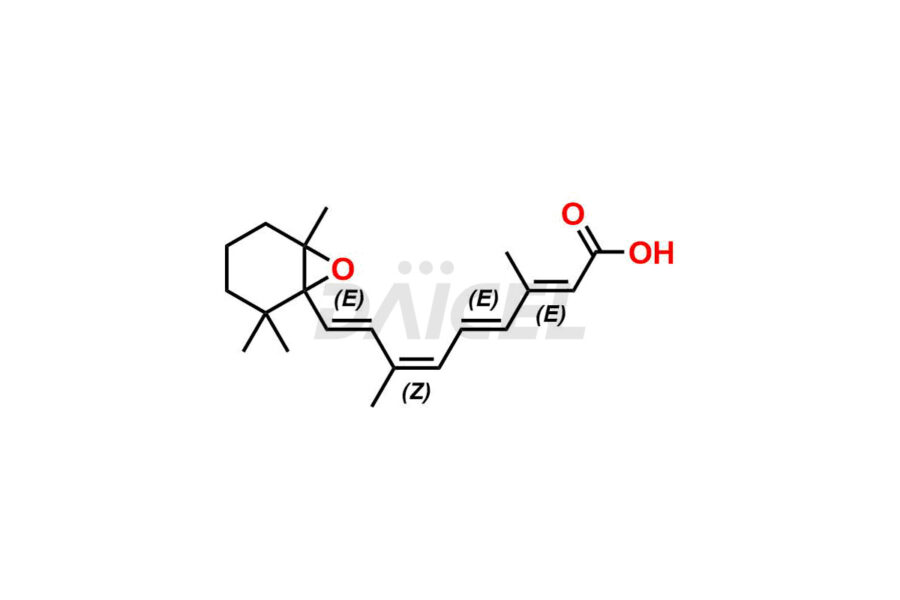
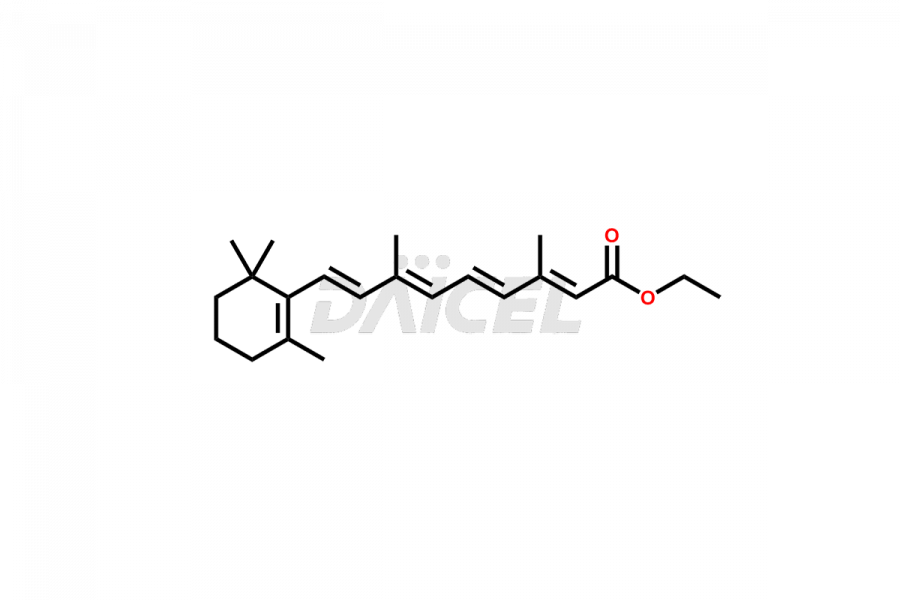
Retinoic Acid
General Information
Retinoic Acid Impurities and Retinoic Acid
Daicel Pharma offers synthesis for Retinoic Acid impurity standards, which include 4-Oxo-9-Cis Retinoic acid, 5,6-Epoxy-9-Cis-Retinoic Acid, and All-trans 5,6-Epoxy Retinoic Acid. The quality, effectiveness, safety, and stability analysis of Retinoic Acid involves the use of these impurity standards.. Daicel Pharma offers custom Retinoic Acid impurities synthesis and delivers them worldwide.
Retinoic Acid [CAS: 302-79-4] is a naturally occurring derivative of retinol, Vitamin A. It is an all-trans-retinoate conjugate acid.
Retinoic Acid: Use and Commercial Availability
Retinoic Acid is for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris, flat warts, and other skin conditions (psoriasis, ichthyosis congenita, ichthyosis vulgaris, lamellar icthyo, etc.). It helps in cell growth and early embryonic development. It also helps in cancer prevention and therapy.
This medication is available in the market under the brand names, Altreno, Avita, Retin-A, Refissa, and more.
Retinoic Acid Structure and Mechanism of Action 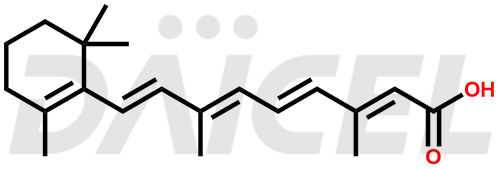
The chemical name of Retinoic Acid is (all-E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid. Its chemical formula is C20H28O2, and its molecular weight is approximately 300.4 g/mol.
The precise mechanism of action of Retinoic Acid is unknown.
Retinoic Acid Impurities and Synthesis
Impurities of Retinoic Acid are unintentional chemical compounds present during the manufacture or storage of retinoic acid, a vitamin A derivative frequently used in dermatology. They may form from raw materials, reagents, intermediates, or degradation products. Retinoic Acid impurities require strict control and monitoring to assure drug safety, efficacy, and quality, and analytical procedures help identify, quantify, and characterize these impurities.
Daicel Pharma provides a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) of Retinoic Acid impurity standards which include 4-Oxo-9-Cis Retinoic acid, 5,6-Epoxy-9-Cis-Retinoic Acid, and All-trans 5,6-Epoxy Retinoic Acid. Our cGMP-certified analytical facility provides a comprehensive CoA with detailed characterization data like 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity. Additional characterizations like 13C-DEPT are available upon request.
References
FAQ's
References
- Solladie, Guy; Girardin, Andre, Highly stereoselective synthesis of vitamin A and all-trans retinoic acid by low-valent titanium induced reductive elimination, Tetrahedron Letters, Volume: 29, Issue: 2, Pages: 213-16, 1988
- Frolik, Charles A.; Tavela, Thomas E.; Peck, Gary L.; Sporn, Michael B., High-pressure liquid chromatographic determination of 13-cis-retinoic acid and all-trans-retinoic acid in human plasma, Analytical Biochemistry, Volume: 86, Issue: 2, Pages: 743-50, 1978
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the acceptable limit of Retinoic Acid impurities?
The acceptable limits for Retinoic Acid impurities defined by regulatory authorities or pharmacopeial standards differ depending on the type of specific impurity and its potential impact on drug safety and efficacy.
Can Retinoic Acid impurities be minimized?
Yes, the presence of Retinoic Acid impurities can be minimized through careful control and monitoring during the manufacturing process and by implementing purification techniques.
What is the regulatory guideline for Retinoic Acid impurities?
The regulatory guideline for Retinoic acid impurities is determined by various regulatory authorities, which provide recommendations and their limits in pharmaceutical substances.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Retinoic Acid impurities?
Retinoic Acid impurities should be stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8°C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.