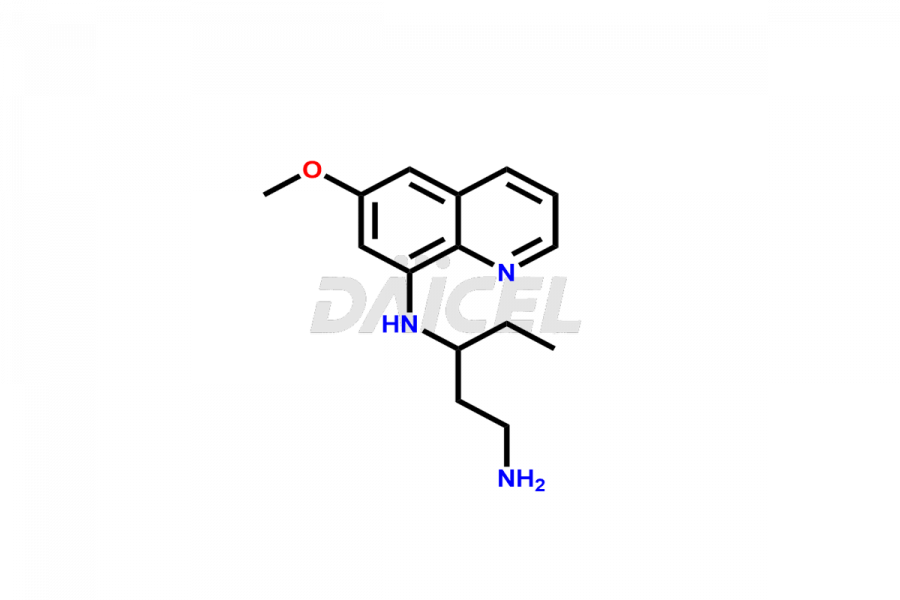
Primaquine
General Information
Primaquine Impurities and Primaquine
Daicel Pharma offers Primaquine impurity standards, including Primaquine Phosphate Impurity and (N3-(6-Methoxyquinolin-8-Yl) Pentane-1,3-Diamine). Their presence can have an impact on the efficacy, quality, and safety of Primaquine. Daicel Pharma custom prepares Primaquine impurities and delivers them globally.
Primaquine [CAS: 90-34-6] is an aminoquinoline compound that treats malaria and Pneumocystis pneumonia, primarily functioning as an antimalarial agent.
Primaquine: Use and Commercial Availability
Primaquine plays a crucial role as an antimalarial agent and prevents malaria relapse. Among the known 8-aminoquinolines, Primaquine treats extracellular forms of malaria from infections caused by P. vivax and P. ovale parasites. This drug is available under Avlon, etc.
Primaquine Structure and Mechanism of Action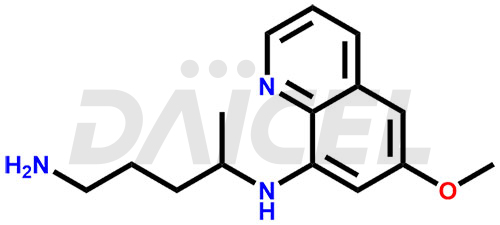
The chemical name of Primaquine is N4-(6-Methoxy-8-quinolinyl)-1,4-pentanediamine. Its chemical formula is C15H21N3O, and its molecular weight is approximately 259.35 g/mol.
The exact mechanism of action of Primaquine is not known.
Primaquine Impurities and Synthesis
Primaquine impurities are undesired compounds found in Primaquine formulations that can occur during the synthetic process1 or be introduced during manufacture or storage. They can impair Primaquine’s quality, safety, and efficacy. As a result, stringent controls are put in place to identify, characterize, and manage impurities within permissible ranges.
Daicel Pharma offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for Primaquine impurity standards, including Primaquine Phosphate Impurity and (N3-(6-Methoxyquinolin-8-Yl) Pentane-1,3-Diamine). Our analytical facility, certified under current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP), provides a comprehensive CoA with detailed characterization data such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity2. We give additional characterization details like 13C-DEPT on request. Our experienced team at Daicel Pharma specializes in synthesizing Primaquine impurities.
References
FAQ's
References
- Talati, S. M.; Latham, M. R.; Moore, E. G.; Hargreaves, G. W.; Blanton, C. DeWitt Jr., Synthesis of potential antimalarials: primaquine analogs, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Volume: 59, Issue: 4, Pages: 491-5, 1970
- Rajagopalan, T. G.; Anjaneyulu, B.; Shanbag, V. D.; Grewal, R. S., Electron-capture gas chromatographic assay for primaquine in blood, Journal of Chromatography, Biomedical Applications Volume: 224, Issue: 2, Pages: 265-73, 1981
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it more probable that Primaquine impurities will be in specific formulations or dosage forms?
The presence of impurities in Primaquine is not necessarily limited to specific formulations or dosage forms, as it depends on various factors such as manufacturing processes and quality control measures implemented by different manufacturers.
Can Primaquine impurities transform or degrade over time, leading to new impurity formation?
Yes, impurities in Primaquine can undergo transformation or degradation over time, potentially resulting in new impurity formation.
What measures are taken to ensure the quality of Primaquine impurity during storage and distribution?
To ensure the purity and quality of Primaquine impurities during storage and distribution, appropriate packaging materials, storage conditions, and quality control processes are implemented to prevent contamination and degradation and maintain product integrity.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Primaquine impurities?
Primaquine impurities are stored preferably at a regulated room temperature of 2-8°C or as specified on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.