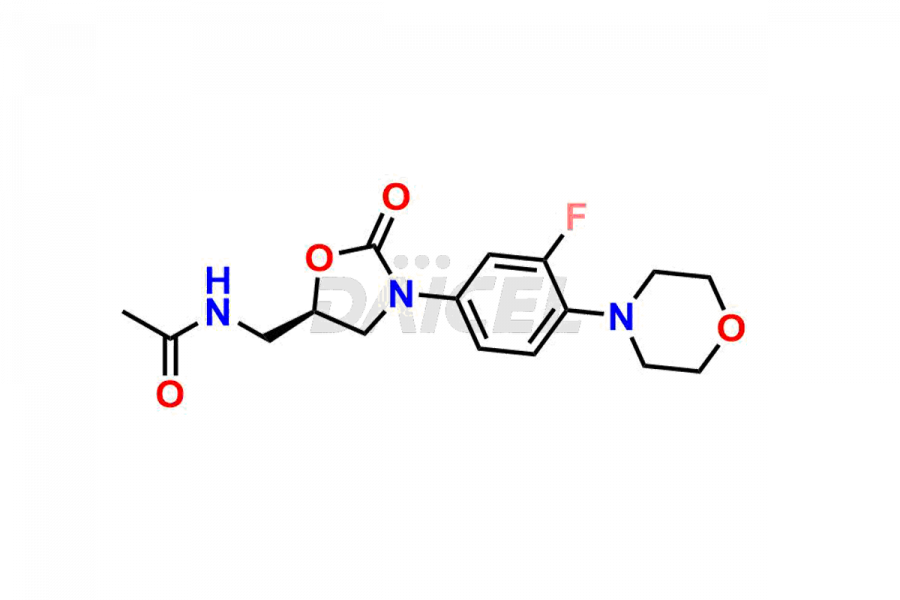
Linezolid
General Information
Linezolid Impurities and Linezolid
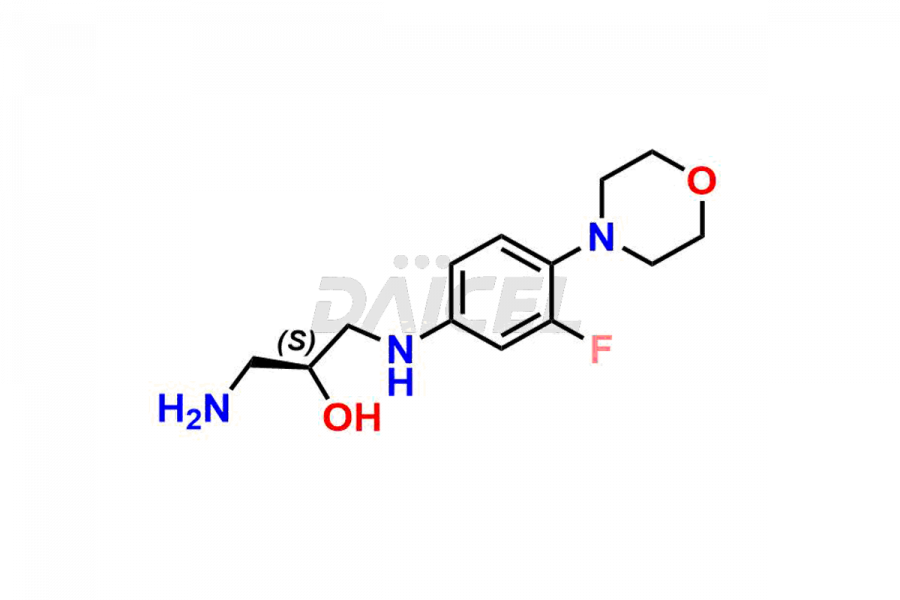
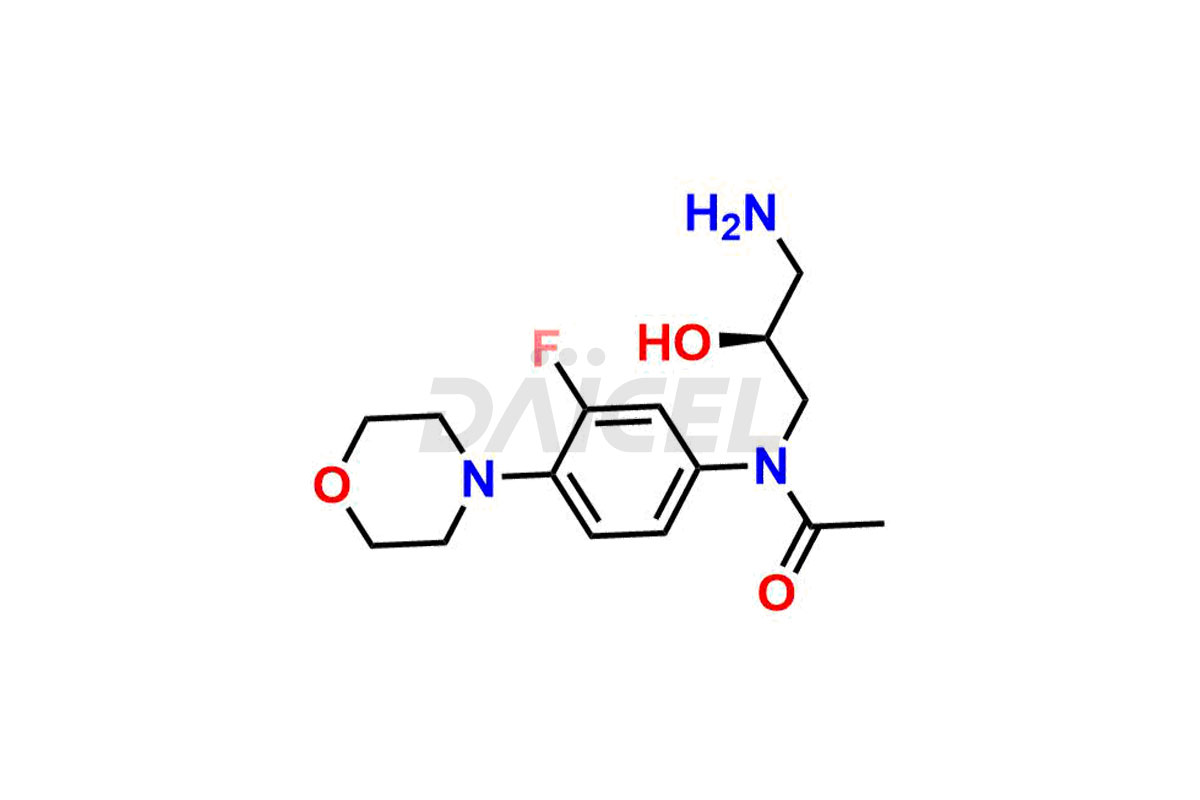
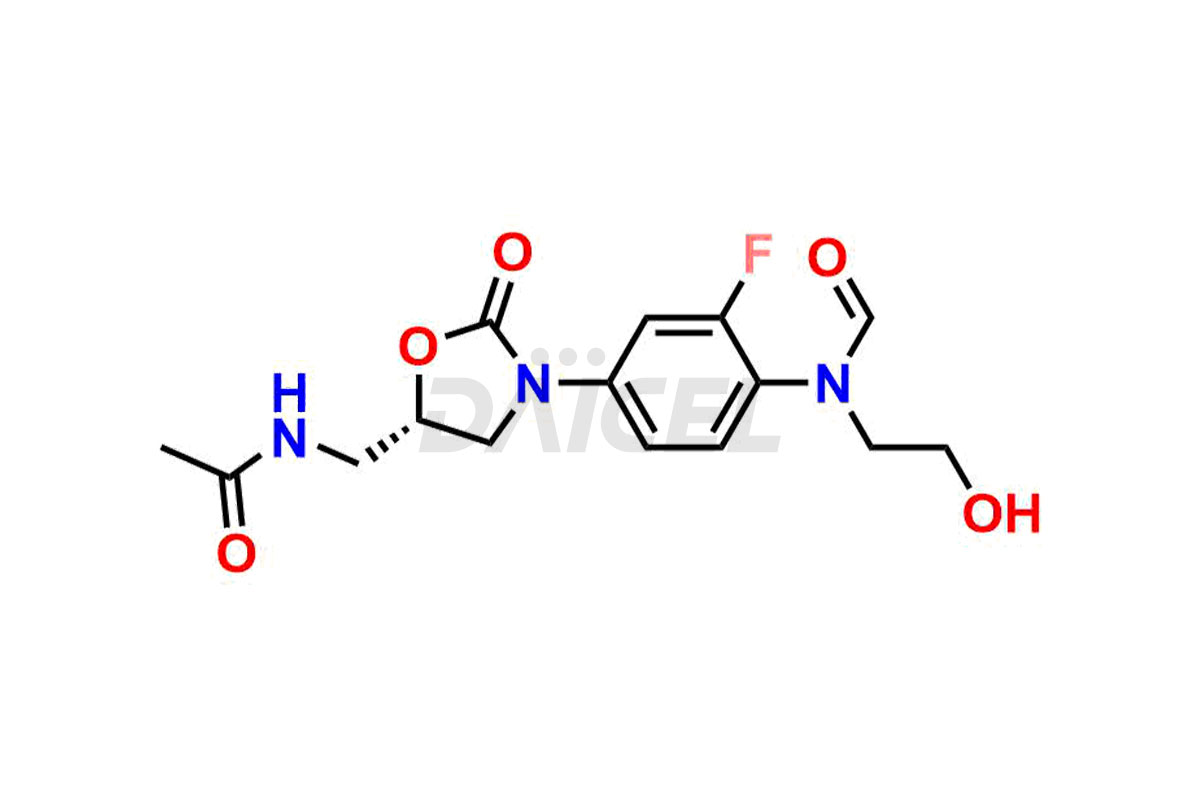
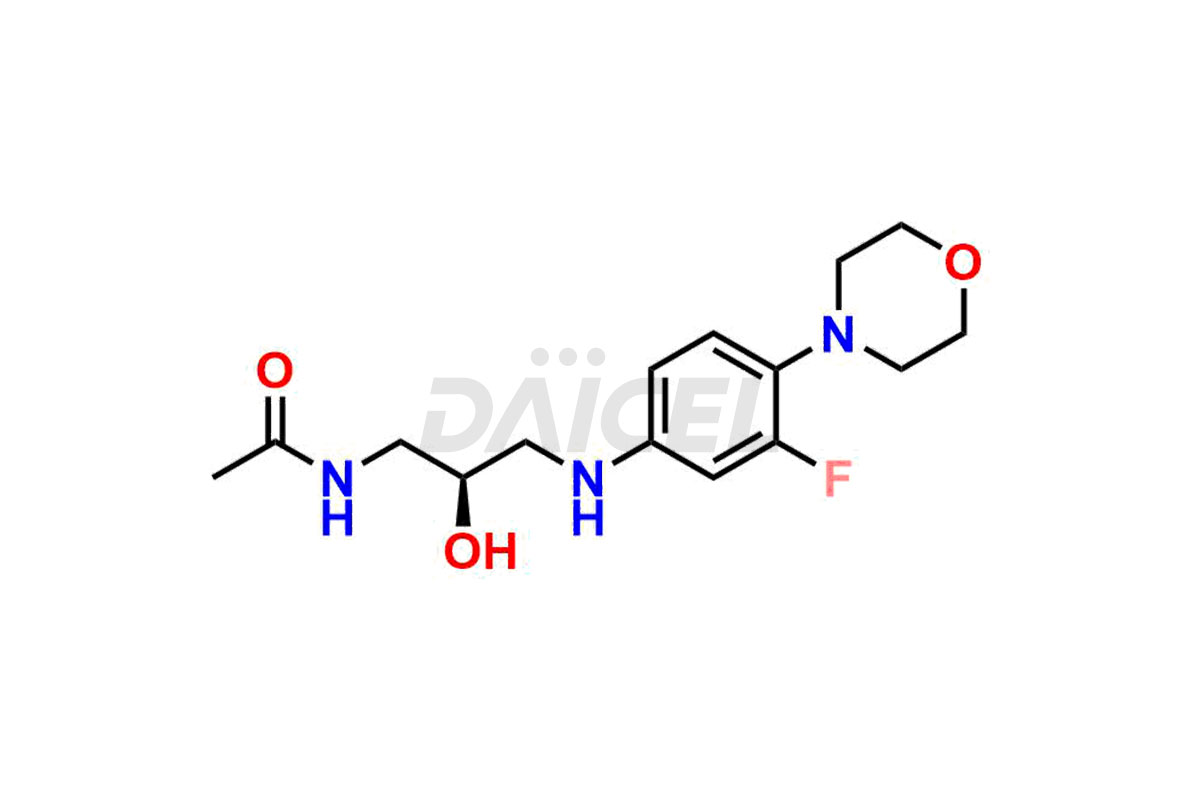
For evaluating the purity and safety of Linezolid, an essential active pharmaceutical ingredient, Daicel Pharma offers a customized synthesis of Linezolid impurity standards. These impurity standards include crucial compounds such as 1-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)-2-methyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-5-ol, Desacetyl-N, O-descarbonyl Linezolid, Linezolid impurity -D, Linezolid impurity -F, Linezolid impurity E, Linezolid R-Isomer, Linezolid Related Compound C, and Linezolid Related Compound D. Additionally, Daicel Pharma provides worldwide delivery options for Linezolid impurity standards.
Linezolid [CAS: 165800-03-3] is a synthetic oxazolidinone derivative that acts as an antibacterial agent by inhibiting an early step in bacterial protein synthesis. It also affects blood pressure by inhibiting monoamine oxidase. This medication treats skin and respiratory tract infections caused by gram-positive bacteria.
Linezolid: Use and Commercial Availability
Zyvox is the brand name under which the drug Linezolid is available. It is a synthetic oxazolidinone antimicrobial drug. Linezolid treats gram-positive infections, including bacterial pneumonia, skin and skin structure infections, and vancomycin-resistant enterococcal (VRE) infections.
Linezolid Structure and Mechanism of Action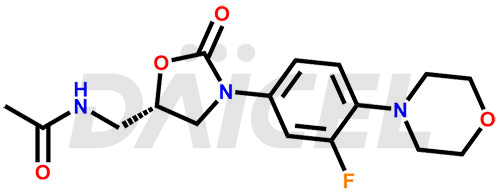
The chemical name of Linezolid is N-[[(5S)-3-[3-Fluoro-4-(4-morpholinyl)phenyl]-2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl]methyl]acetamide. Its chemical formula is C16H20FN3O4, and its molecular weight is approximately 337.35 g/mol.
Linezolid inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by preventing a functional 70S initiation complex formation that causes the bacterial translation process.
Linezolid Impurities and Synthesis
Impurities in Linezolid are unwanted substances that may be present in the drug product with the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). They can originate from manufacturing1,2, starting materials, or interactions with environmental factors. The common impurities in Linezolid include related substances, degradation products, residual solvents, and process-related impurities. It is essential to monitor and control the impurity levels to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of the Linezolid drug product. Regulatory authorities have set specific guidelines and limits for impurity levels to maintain purity and minimize potential risks associated with the drug. Stringent quality control measures throughout manufacturing minimize impurity levels and ensure product integrity.
Daicel Pharma strictly adheres to cGMP standards and operates an analytical facility for the preparation of Linezolid impurity standards, which include 1-(3-fluoro-4-morpholinophenyl)-2-methyl-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidin-5-ol, Desacetyl-N, O-descarbonyl Linezolid, Linezolid impurity -D, Linezolid impurity -F, Linezolid impurity E, Linezolid R-Isomer, Linezolid Related Compound C, and Linezolid Related Compound D. Our Linezolid impurity standards have a detailed Certificate of Analysis (CoA) that provides a comprehensive characterization report. This report includes data obtained through techniques, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity analysis3. Upon request, we give additional data like 13C-DEPT. Moreover, we can synthesize unknown Linezolid impurity standards and degradation products. Each delivery has a comprehensive characterization report.
References
FAQ's
References
- Barbachyn, Michael R.; Brickner, Steven J.; Hutchinson, Douglas K., Substituted Oxazine And Thiazine Oxazolidinone Antimicrobials, Upjohn Co., United States,EP717738B1, October 20, 1999
- Brickner, Steven J.; Hutchinson, Douglas K.; Barbachyn, Michael R.; Manninen, Peter R.; Ulanowicz, Debra A.; Garmon, Stuart A.; Grega, Kevin C.; Hendges, Susan K.; Toops, Dana S, Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of U-100592 and U-100766, Two Oxazolidinone Antibacterial Agents for the Potential Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, Volume: 39, Issue: 3, Pages: 673-9, 1996
- Peng, Geoffrey W.; Stryd, Ronald P.; Murata, Shoiji; Igarashi, Mayumi; Chiba, Koji; Aoyama, Hiroyuki; Aoyama, Makiko; Zenki, Tomoko; Ozawa, Naoki, Determination of linezolid in plasma by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography, Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, Volume: 20, Issue: 1-2, Pages: 65-73, 1999
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Linezolid impurities vary from batch to batch?
Yes, the presence and levels of impurities in Linezolid can vary from batch to batch due to variations in the process, raw materials, and other factors. However, manufacturers aim to maintain consistent quality and minimize impurity levels within acceptable limits.
Are there specific methods used to detect and quantify Linezolid impurities?
Yes, analytical methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS) are commonly employed to detect and quantify impurities in Linezolid. These methods allow for accurate assessment and control of impurity levels.
Which solvent helps in analyzing Linezolid impurities?
Methanol is a solvent used when analyzing many impurities in Linezolid.
What is the recommended storage temperature for Linezolid impurities?
Linezolid impurities should be stored, at a controlled room temperature, usually between 2-8 °C.
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.