Fosfomycin
General Information
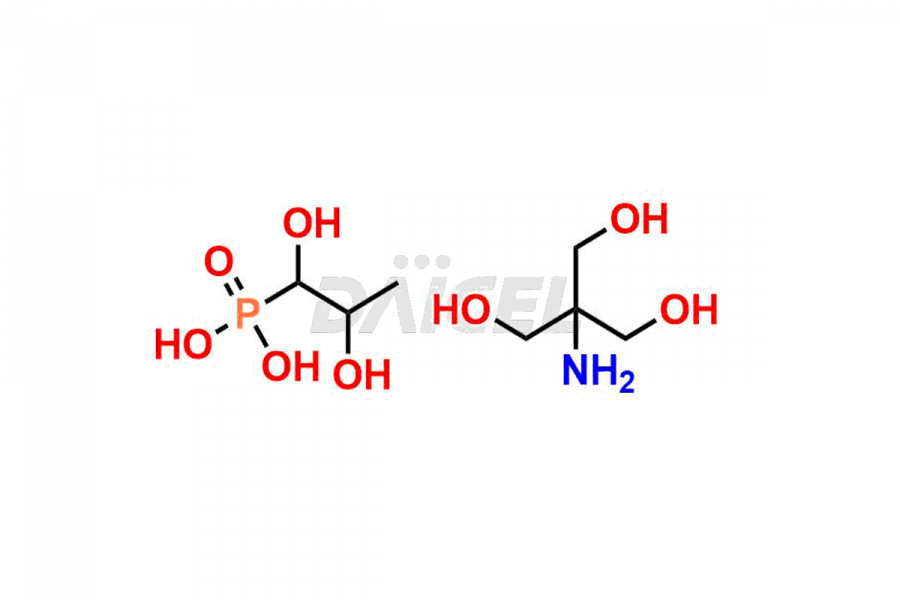
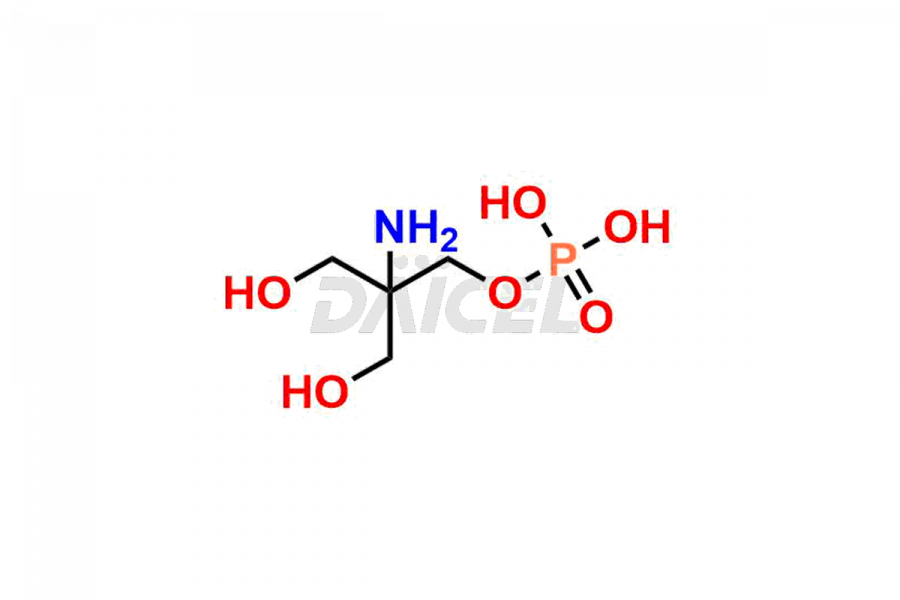
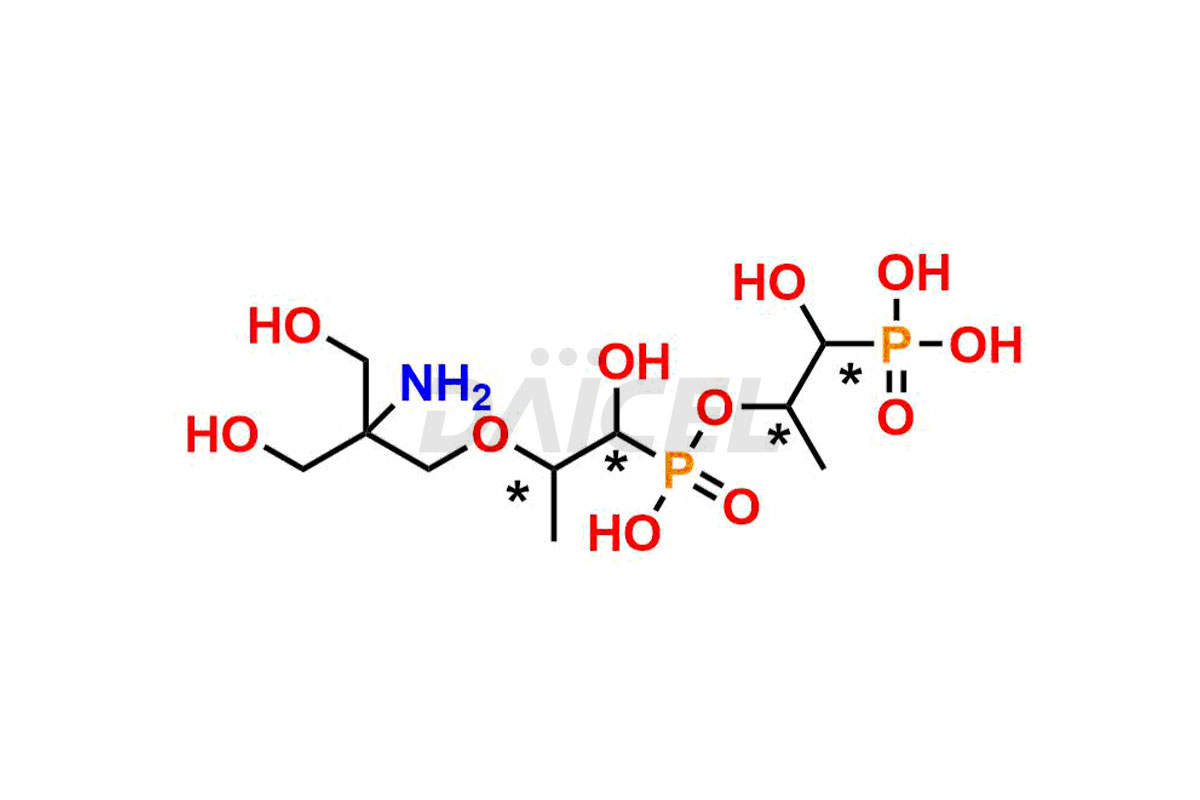
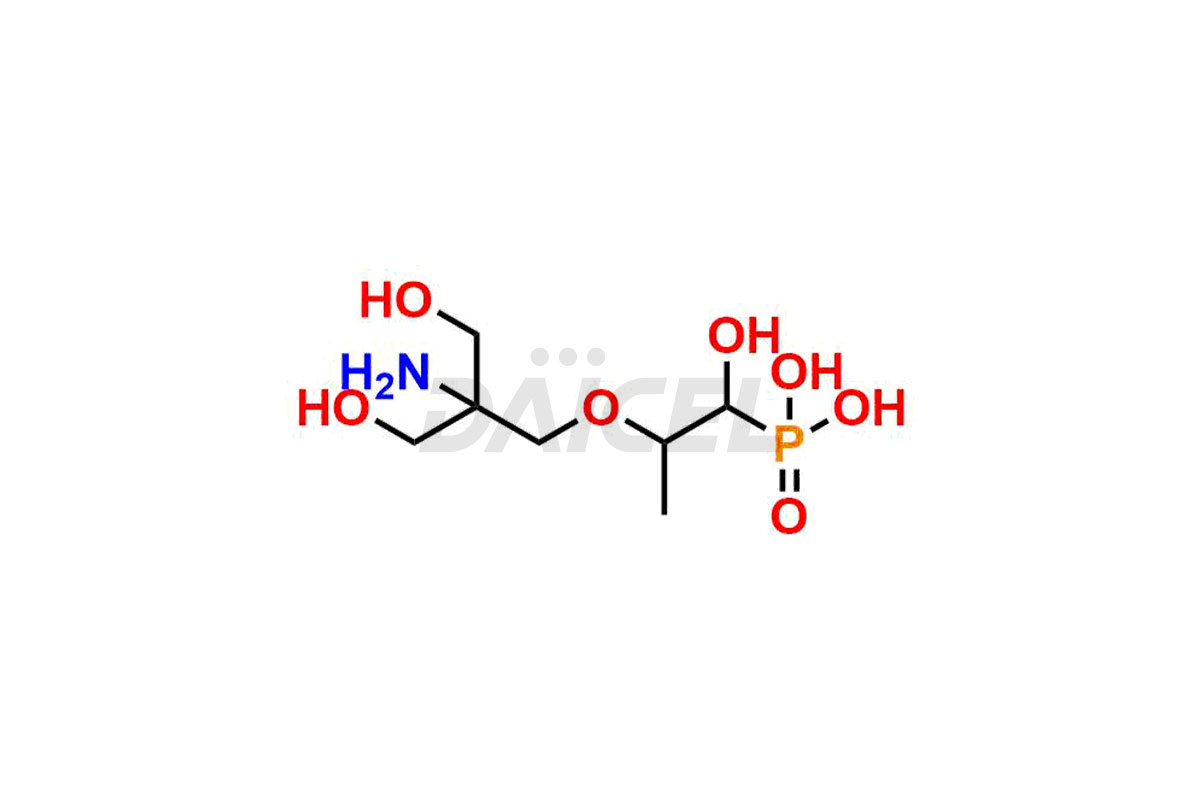
Fosfomycin Impurities and Fosfomycin
Daicel Pharma synthesizes high-quality Fosfomycin impurities, Fosfomycin EP Impurity-A Tromethamine Salt, Fosfomycin EP Impurity-C, Fosfomycin Impurity D, and Fosfomycin Tromethamine Adduct, which are crucial in the analysis of the quality, stability, and biological safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient Fosfomycin. Moreover, Daicel Pharma offers custom synthesis of Fosfomycin impurities and delivers them globally.
Fosfomycin [CAS: 23155-02-4] is a synthetic antibiotic with broad-spectrum properties that treat uncomplicated urinary tract infections as it has bactericidal and antimicrobial properties.
Fosfomycin: Use and Commercial Availability
Fosfomycin is a medicine that treats uncomplicated urinary tract infections caused by certain bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis. Fosfomycin is available under the trade names Fosfomycin Tromethamine and Monurol.
Fosfomycin Structure and Mechanism of Action 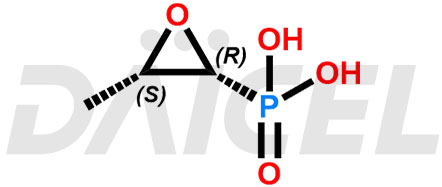
The chemical name of Fosfomycin is P-[(2R,3S)-3-Methyl-2-oxiranyl]phosphonic acid. Its chemical formula is C3H7O4P, and its molecular weight is approximately 138.06 g/mol.
The bactericidal action of Fosfomycin inactivates the enzyme enolpyruvyl transferase, blocking bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Fosfomycin Impurities and Synthesis
Various impurities form during manufacturing1,2, storage, or degradation of Fosfomycin. These impurities occur through different pathways, such as hydrolysis, oxidation, or degradation of the active ingredient. They affect Fosfomycin quality, safety, and efficacy and should be monitored and controlled during synthesis.
Daicel offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from a cGMP-compliant analytical facility for Fosfomycin impurity standards, Fosfomycin EP Impurity-A Tromethamine Salt, Fosfomycin EP Impurity-C, Fosfomycin Impurity D, and Fosfomycin Tromethamine Adduct. The CoA includes characterization data, such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS3, and HPLC purity4. We give a complete characterization report on delivery. Daicel has the technology and expertise to prepare any unknown Fosfomycin impurity or degradation product.
References
FAQ's
References
- Hendin, David; Stapley, Edward O.; Martinez Mata, Justo; Mochales del Val, Sagrario, Antibacterial Composition Containing (-) (Cis-1 2-Epoxypropyl) Phosphoric Acid, Merck and Co., Inc., US3639590A, February 1, 1972
- Christensen, Burton G.; Leanza, W. J.; Beattie, T. R.; Patchett, A. A.; Arison, B. H.; Ormond, Robert E.; Kuehl, Frederick A. Jr.; Albers-Schonberg, G.; Jardetzky, O., Phosphonomycin: structure and synthesis, Science (Washington, DC, United States),Volume: 166, Issue: 3901, Pages: 123-5,1969
- Shafer, H.; Vandenheuvel, W. J. A.; Ormond, R.; Kuehl, F. A.; Wolf, Frank James, Characterization of phosphonomycin by microchromatographic and related techniques, Journal of Chromatography, Volume: 52, Issue: 1, Pages: 111-17, 1970
- Gazzani, Gabriella; Stoppini, Giovanna; Gandini, Carlo; Bettero, Antonio, Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic and derivative UV spectrophotometric determination of α-phenylethylamine in phosphomycin, Journal of Chromatography, Volume: 609,Issue: 1-2,Pages: 391-4, 1992
Frequently Asked Questions
How are impurities typically controlled in Fosfomycin?
Fosfomycin impurities are controlled through rigorous testing and analysis throughout the drug development process. It includes identifying and determining their potential risks, establishing acceptable limits, and developing analytical methods to detect and measure impurities
How can Fosfomycin Impurities be detected?
Fosfomycin impurities can be detected using various analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).
Which solvent helps in the analysis of Fosfomycin impurities?
Water is a solvent that helps in analyzing most of the Fosfomycin impurities.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Fosfomycin impurities?
Fosfomycin impurities are stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8 ⁰C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.