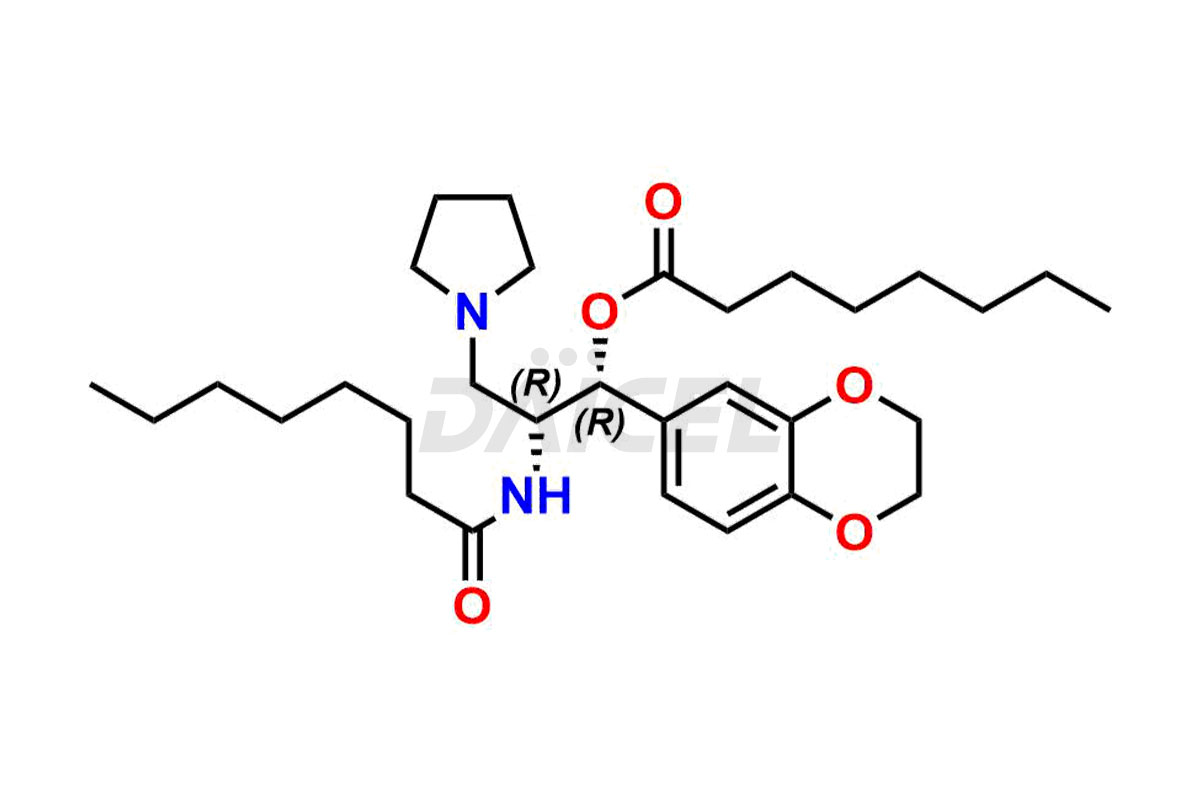
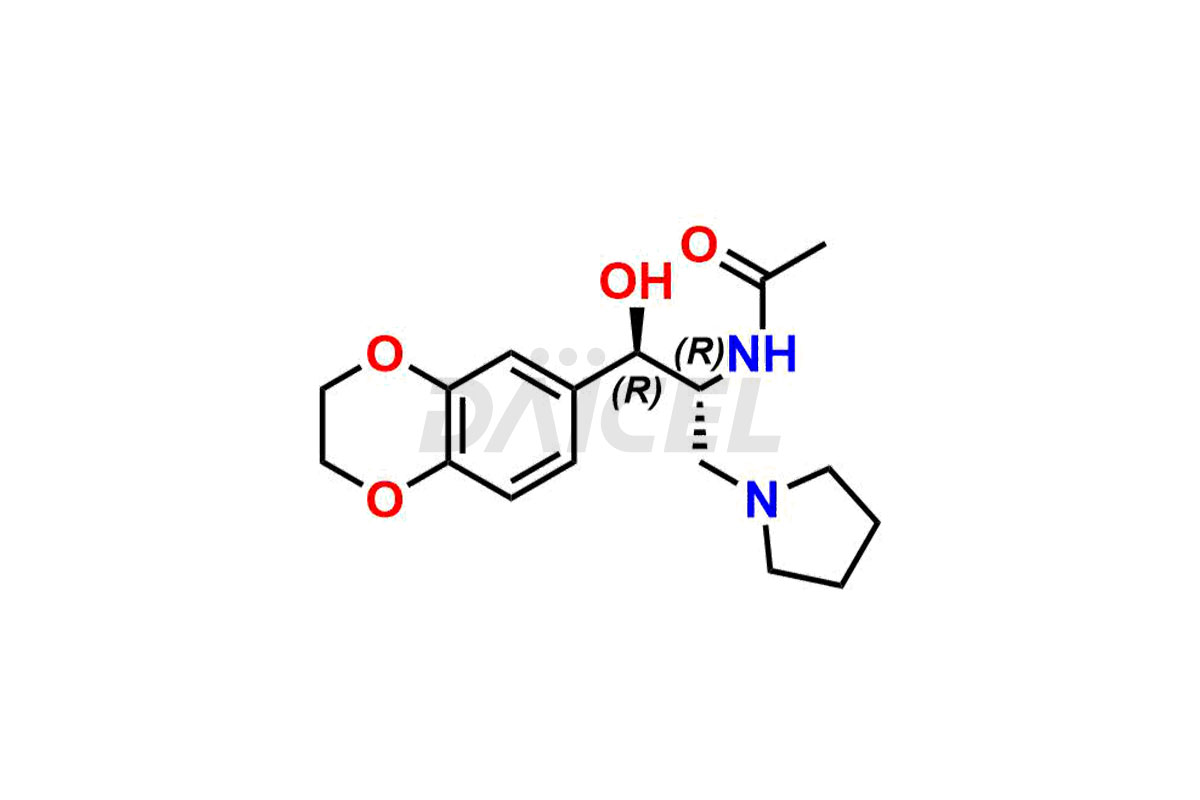
Eliglustat
References
- Hirth, Bradford H.; Siegel, Craig, A N-Acylsphingosine Glucosyltransferase Inhibitor, Genzyme Corporation, United States, EP1409467B1, April 18, 2012
- Umamaheshwar Puppala,Koduri S V Srinivas,K Venkateshwara Reddy,Muralidharan Kaliyaperumal,Raju Doddipalla &Bhaskar Rao Jogi, Isolation and Characterization of Novel Degradation Products of Eliglustat Tartrate Using 2D-NMR and HRMS: Development and Validation of Stability Indicating RP-UPLC Method for Quantification of Assay and Characterized Impurities, Analytical Chemistry Letters,Volume 10, 2020 - Issue 1, Pages 1-20
Frequently Asked Questions
How can the formation of Eliglustat impurities be minimized?
The formation of Eliglustat impurities is minimized by optimizing reaction conditions, employing suitable purification techniques, ensuring proper storage and handling, and conducting stability studies to understand degradation pathways.
Can Eliglustat impurities impact the drug's efficacy?
Impurities in Eliglustat can potentially impact its efficacy by altering the drug's pharmacokinetics, stability, or interaction with the target receptors. Hence, their control is essential to maintain the desired therapeutic effect.
What are the challenges in analyzing Eliglustat impurities?
Analyzing Eliglustat impurities can be challenging due to their low concentrations, potential complexity, and the need for sensitive and specific analytical techniques. Validation of analytical methods is crucial for accurate impurity detection.
How should Eliglustat impurities be stored in terms of temperature?
Eliglustat impurities are stored at a controlled room temperature, 2-8 °C, or under a Nitrogen atmosphere. You can refer to the storage on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA) specifications.
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.