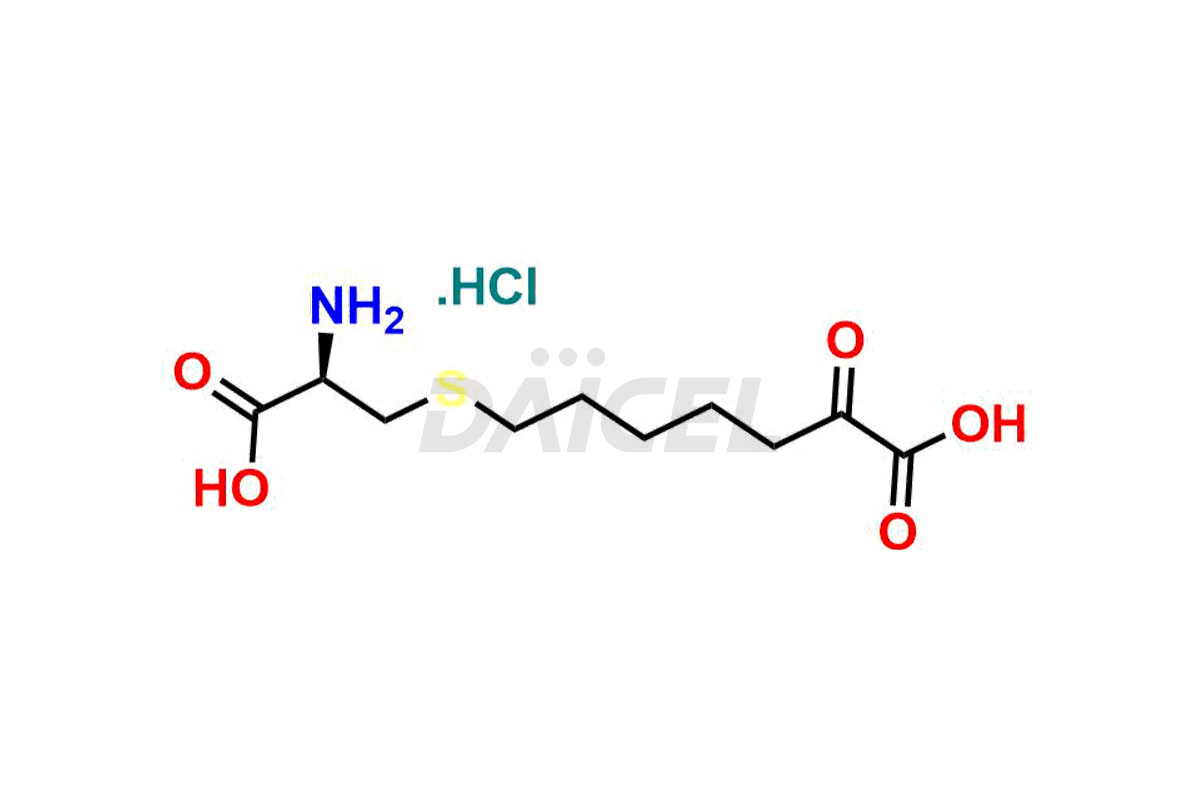
Cilastatin
General Information
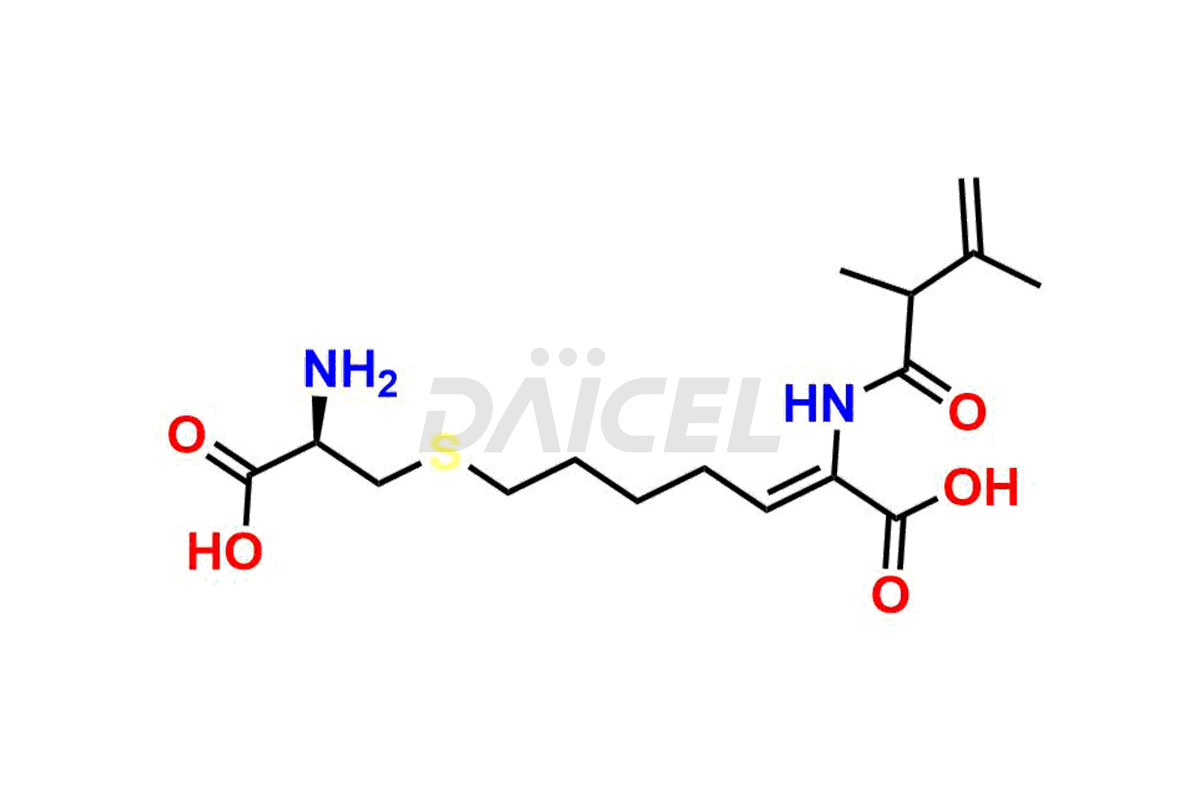
Cilastatin Impurities and Cilastatin
Daicel Pharma synthesizes Cilastatin impurities of exceptional quality, such as Cilastatin EP impurity-E and Cilastatin EP impurity-F. These impurities are crucial to assess the purity, reliability, and safety of an active pharmaceutical ingredient, Cilastatin. Besides, Daicel Pharma provides custom synthesis of Cilastatin impurities to meet clients’ demands for delivery worldwide.
Cilastatin [CAS: 82009-34-5] is a compound that inhibits renal dehydropeptidase, an enzyme involved in the breakdown of thienamycin beta-lactam antibiotics and the conversion of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4. It is a non-proteinogenic L-alpha-amino acid, specifically a derivative of L-cysteine.
Cilastatin: Use and Commercial Availability
Cilastatin, a nephroprotectant, and inhibitor of dehydropeptidase, is administered in conjunction with imipenem to prevent inadequate levels of the antibiotic. Imipenem functions by permeating the bacterial cell membrane and binding to penicillin-binding proteins, thereby hindering the synthesis of the cell wall, leading to bacterial cell death. Cilastatin competitively inhibits dehydropeptidase, an enzyme responsible for the renal metabolism of imipenem. The combined therapeutic effect of Cilastatin and imipenem encompasses the treatment of various bacterial infections, such as respiratory, skin, bone, gynecologic, urinary tract, and intra-abdominal infections, as well as septicemia and endocarditis. Cilastatin with imipenem formulations is available under brand names, including Primaxin and Recarbrio.
Cilastatin Structure and Mechanism of Action 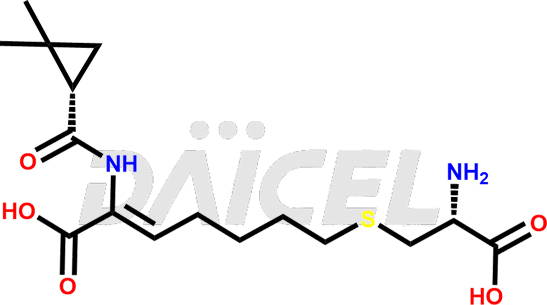
The chemical name of Cilastatin is (2Z)-7-[[(2R)-2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl]thio]-2-[[[(1S)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropyl]carbonyl]amino]-2-heptenoic acid. Its chemical formula is C16H26N2O5S, and its molecular weight is approximately 358.5 g/mol.
Cilastatin inhibits renal dehydropeptidase-I, an enzyme responsible for renal metabolism, and prevents both inactivation and toxicity.
Cilastatin Impurities and Synthesis
During the synthesis1, storage, or degradation of Cilastatin, an inhibitor of renal dehydropeptidase, impurities may form. They can arise from starting materials, intermediates, or side reactions. It is essential to analyze and control these impurities to ensure the safety and efficacy of the drug. Impurity analysis helps identify and quantify these substances, enabling manufacturers to establish acceptable limits and implement control strategies. By monitoring and controlling Cilastatin impurities, the quality, purity, and stability can be maintained, ensuring its effectiveness and minimizing potential risks.
Daicel Pharma offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for Cilastatin impurity standards, such as Cilastatin EP impurity-E and Cilastatin EP impurity-F, generated from an analytical facility compliant with cGMP standards. The CoA includes a comprehensive characterization report comprising data from techniques like 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity2. Furthermore, on request, we give additional data like 13C-DEPT and CHN. Daicel Pharma can create unknown Cilastatin impurities or degradation products. A complete characterization report accompanies every delivery.
References
FAQ's
References
- Kahan, Frederick M.; Kropp, Helmut, Combination of thienamycin-type antibiotics with dipeptidase inhibitors, Merck and Co., Inc., United States, US4539208A, September 3, 1985
- Demetriades, J. L.; Souder, P. R.; Entwistle, L. A.; Vincek, W. C.; Musson, D. G.; Bayne, W. F., High-performance liquid-chromatographic determination of cilastatin in biological fluids, Journal of Chromatography, Biomedical Applications, Volume: 382, Pages: 225-31, 1986
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the measures to control Cilastatin impurities?
Control measures include adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMP), process optimization, proper storage conditions, and monitoring impurity levels.
What is the role of stability studies in impurity control for Cilastatin?
Stability studies assess the degradation pathways of Cilastatin, identify impurities formed over time, and help establish appropriate storage conditions to control impurity formation.
Which solvent helps in the analysis of Cilastatin impurities?
Water is a solvent used in analyzing many impurities in Cilastatin.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Cilastatin impurities?
Cilastatin impurities are stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8 °C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.