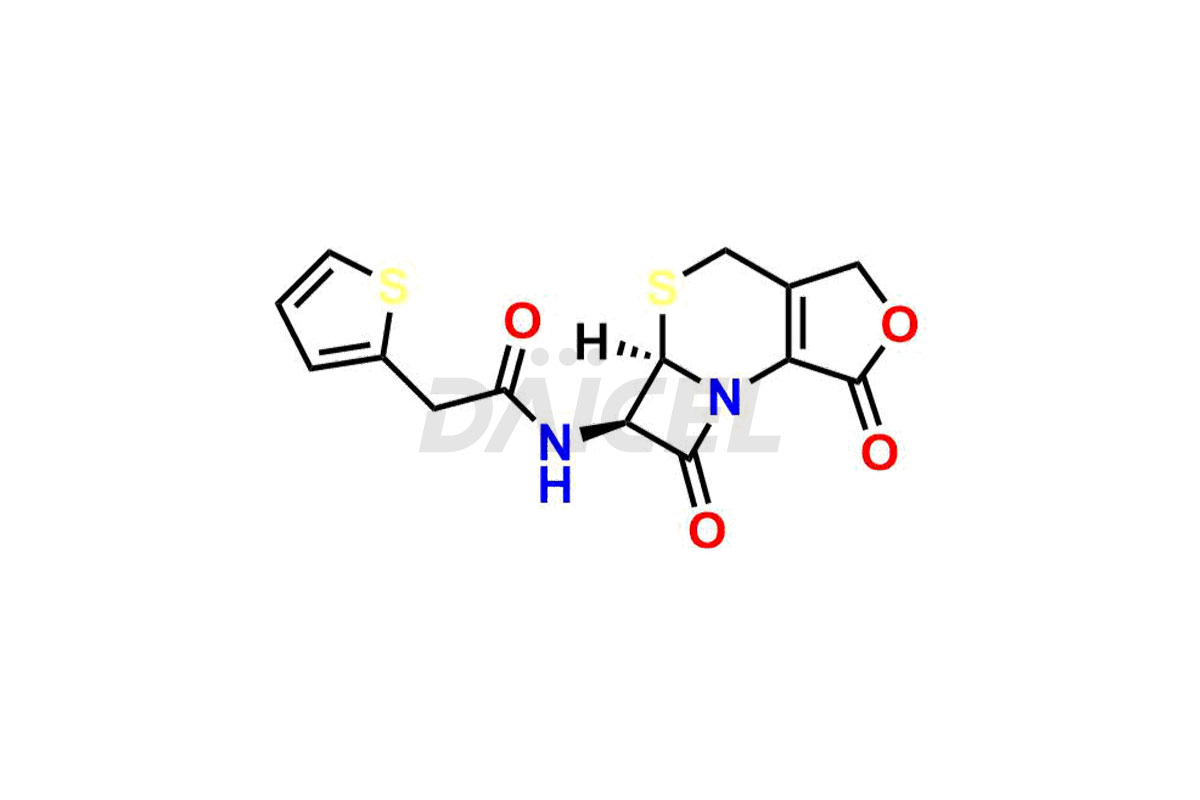
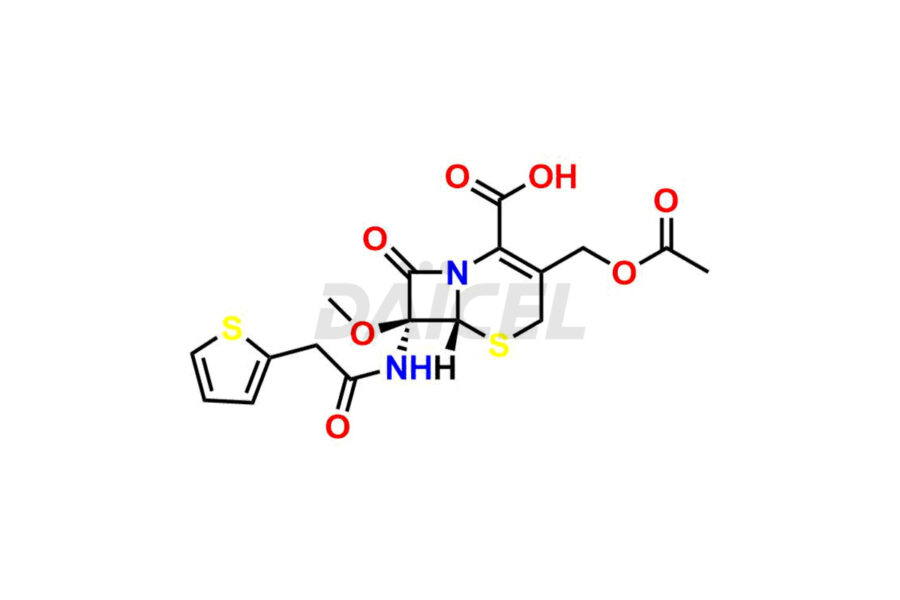
Cefalotin
General Information
Cefalotin Impurities and Cefalotin
Daicel Pharma synthesizes high-quality Cefalotin impurities, Cefalotin lactone, and Methoxy Cefalotin Impurity, which are crucial in the analysis of the quality, stability, and biological safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient, Cefalotin. Moreover, Daicel Pharma offers custom synthesis of Cefalotin impurities and delivers them globally.
Cefalotin [CAS: 153-61-7] is an antibacterial drug belonging to the first-generation cephalosporin class of antibiotics. It is a semisynthetic beta-lactam antibiotic that kills bacteria. It is used parenterally during surgery and to treat blood infections. In addition, Cefalotin is an antimicrobial agent.
Cefalotin : Use and Commercial Availability
Cefalotin treats bacterial infections affecting the urinary tract, lower respiratory tract, soft tissues, bones, and joints, skin infections, peritonitis, sepsis, osteomyelitis, mastitis, post-operative infections, and infected wounds. It is available worldwide under brand names such as Arecamin, Baccef, Cefadin, Ceftina, Ceporacin, Cepovenin, Falot, Jnflin, and Practogen, etc.
Cefalotin Structure and Mechanism of Action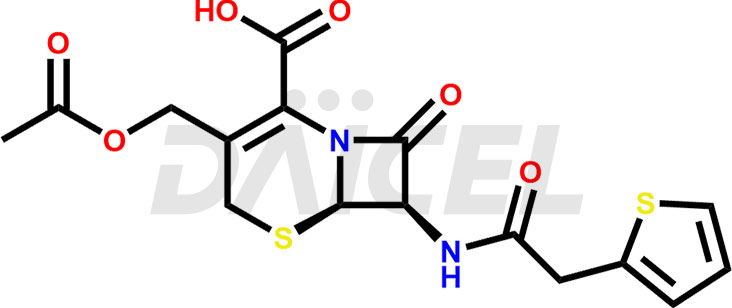
The chemical name of Cefalotin is 3-(Acetoxymethyl)-8-oxo-7-[2-(2-thienyl)acetamido]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is C16H16N2O6S2, and its molecular weight is approximately 396.4g/mol.
Cefalotin binds to penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) located on the inner membrane of bacterial cells. Inactivation of PBPs causes a weakening of the bacterial cell wall and eventual lysis of the bacterial cell.
Cefalotin Impurities and Synthesis
During the anufacturing1 process of Cefalotin, impurities2 may form in the drug that pose potential health risks to patients. These impurities may form due to degradation or by-products of reaction intermediates, including epimeric impurities and degradation products. It is vital to monitor impurity levels in medication to ensure its safety and effectiveness in treating patients.
Daicel offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from a cGMP-compliant analytical facility for Cefalotin impurity standards, Cefalotin lactone, and Methoxy Cefalotin impurity. The CoA includes complete characterization data, such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity. We also provide 13C-DEPT and CHN on request. We give a complete characterization report on delivery.
Daicel has the technology and expertise to prepare any unknown Cefalotin impurity or degradation product. We also provide labeled compounds to quantify the efficacy of generic Cefalotin. Daicel offers highly pure isotope-labeled standards of Cefalotin for bioanalytical research and BA/BE studies with isotope data in CoA.
References
FAQ's
References
Frequently Asked Questions
How are Cefalotin impurities synthesized?
Cefalotin Impurities synthesis is through various chemical reactions such as hydrolysis, oxidation, and deamination of Cefalotin and its intermediates.
How are Cefalotin impurities identified and quantified?
Analytical methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) help to identify and quantify Cefalotin.
Are there any challenges associated with synthesizing Cefalotin impurities?
Synthesis of impurities of Cefalotin is challenging due to the complexity of the chemical reactions involved and the need for specialized equipment and expertise.
Are there any alternative methods for synthesizing Cefalotin impurities?
The alternative methods for synthesizing Cefalotin impurities include using microbial enzymes and biocatalysis.
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.