Carbamazepine
General Information
Carbamazepine Impurities and Carbamazepine
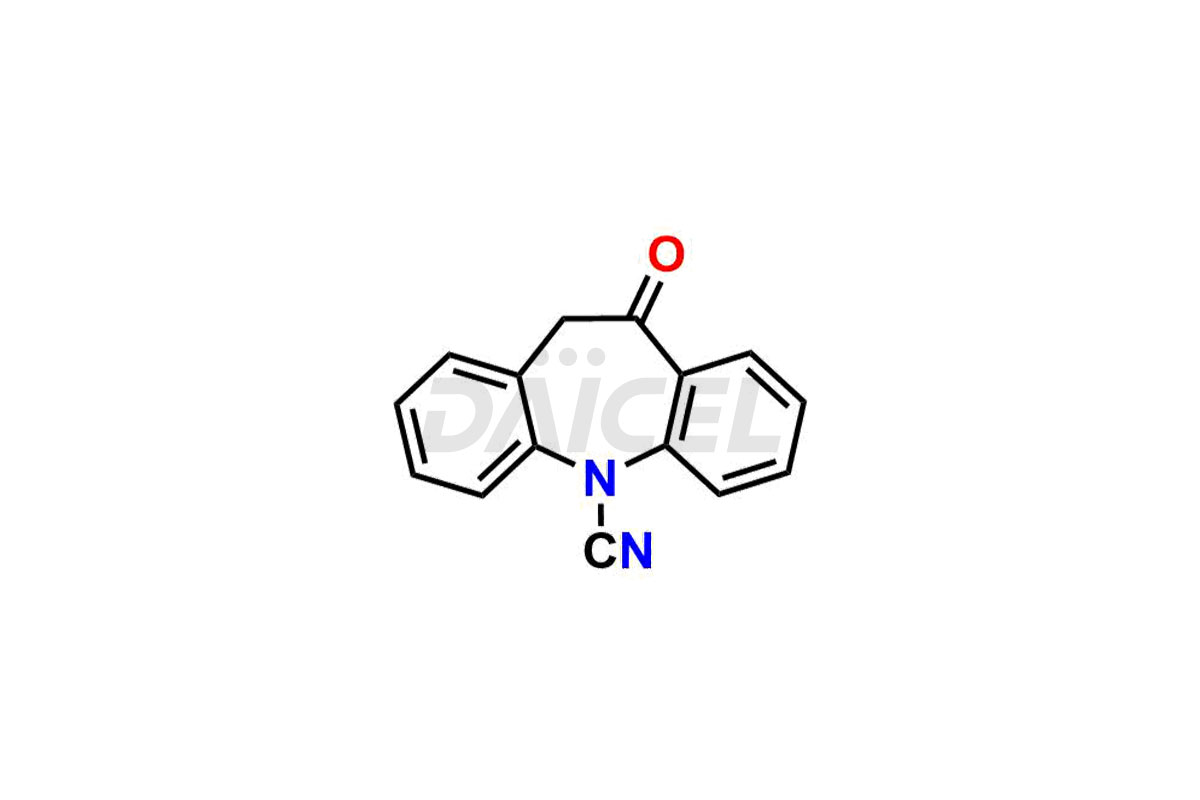
Daicel Pharma synthesizes Carbamazepine impurities of exceptional quality, such as 10-oxo-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine-5-carbonitrile, and Carbamazepine EP Impurity A. These impurities are crucial to assess the purity, reliability, and safety of Carbamazepine, an active pharmaceutical ingredient. Besides, Daicel Pharma provides custom synthesis of Carbamazepine impurities to meet clients’ demands for delivery worldwide.
Carbamazepine [CAS: 298-46-4] is a widely used aromatic anticonvulsant medication for treating epilepsy and trigeminal neuralgia. It is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) with anticonvulsant and analgesic properties. This tricyclic compound is effective in reducing seizures and providing pain relief for patients with neuropathic pain.
Carbamazepine: Use and Commercial Availability
Carbamazepine is an FDA-approved medication for treating various conditions, including epilepsy, trigeminal neuralgia, and acute manic and mixed episodes of bipolar I disorder. It manages partial seizures with complex symptomatology, generalized tonic seizures, and mixed seizure patterns. Carbamazepine is also a first-line treatment for trigeminal neuralgia or tic douloureux. It is available under various brand names, including Carbatrol, Carnexiv, Epitol, Equetro, Tegretol, and Teril.
Carbamazepine Structure and Mechanism of Action 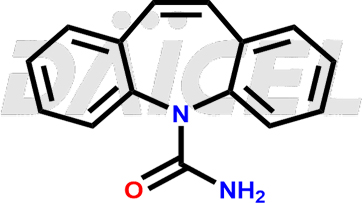
The chemical name of Carbamazepine is 5H-Dibenz[b,f]azepine-5-carboxamide. Its chemical formula is C15H12N2O, and its molecular weight is approximately 236.27 g/mol.
The mechanism of action of Carbamazepine is unknown.
Carbamazepine Impurities and Synthesis
Carbamazepine can undergo degradation and impurity formation under certain conditions, such as exposure to light, high temperature, and moisture. These impurities can affect the drug’s stability, efficacy, and safety. Thus, it is essential to control and monitor the impurities’ formation during the manufacturing1, storage, and transportation of Carbamazepine products. Various methods are employed to minimize the impurities by using appropriate storage conditions, processing parameters, and analytical techniques to detect and quantify them.
Daicel Pharma offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for Carbamazepine impurity standards, such as 10-oxo-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine-5-carbonitrile, and Carbamazepine EP Impurity A, generate from an analytical facility compliant with cGMP standards. The CoA includes a comprehensive characterization report comprising data from techniques like 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity2. Furthermore, on request, we can provide additional data like 13C-DEPT and CHN. Daicel Pharma can synthesize unknown Carbamazepine impurities or degradation products. A complete characterization report accompanies every delivery.
References
FAQ's
Frequently Asked Questions
How can carbamazepine impurities be detected?
Carbamazepine impurities can be detected using various analytical methods such as HPLC and LC-MS/MS.
What are the most common sources of carbamazepine impurities?
The most common sources of Carbamazepine impurities include starting materials, reagents, and solvents used during synthesis.
Which solvent helps in the analysis of Carbamazepine impurities?
Methanol is a solvent used in analyzing many impurities in Carbamazepine.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Carbamazepine impurities?
Carbamazepine impurities are stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8 °C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.