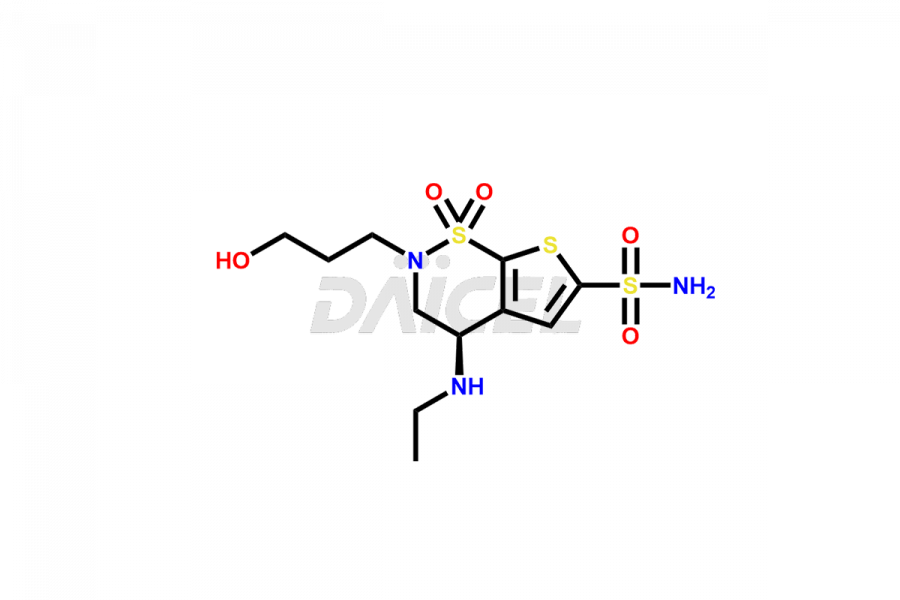
Brinzolamide
References
- Dean, Thomas R.; Chen, Hwang Hsing; May, Jesse A., Thiophene sulfonamides useful as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, Alcon Laboratories, Inc., United States, US5153192A, October 6, 1992
- Balakrishna, Tiwari; Mrunal, K. Shirsat; Amol, Kulkarni, Analytical method development and validation for the determination of Brinzolamide by RP-HPLC, Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, Volume: 10, Issue: 1, Pages: 92-96, 2020
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the methods used to control Brinzolamide impurities?
Various methods are used to control impurities in Brinzolamide, such as controlling the manufacturing process, using appropriate packaging and storage conditions, and using analytical methods to detect and quantify impurities.
Can impurities in Brinzolamide affect its therapeutic efficacy?
Yes, impurities in Brinzolamide can affect its therapeutic efficacy and alter the pharmacological activity and bioavailability of the drug, leading to adverse effects or reduced efficacy.
Which solvent helps in the analysis of Brinzolamide impurities?
Acetonitrile is a solvent used in analyzing many impurities in Brinzolamide.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Brinzolamide impurities?
Brinzolamide impurities are stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8 °C or -20°C, depending on the stability of the impurity, as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.