Abacavir
General Information
Abacavir Impurities and Abacavir
Daicel Pharma synthesizes high-quality Abacavir impurity, N6-Cyclopropyl-9H-Purin-2,6-diamine, which is crucial in analyzing the quality, stability, and biological safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient Abacavir. Moreover, Daicel Pharma offers custom synthesis of Abacavir impurities and delivers them globally.
Abacavir [CAS: 136470-78-5] is a synthetic carbocyclic nucleoside analog treating HIV infection in adults, children, and infants. It combines with other medications for HIV, particularly sulfate and other antiretroviral drugs. Abacavir works as a nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), which helps to combat HIV by inhibiting the activity of the reverse transcriptase enzyme of HIV-1 that is necessary for the virus to replicate.
Abacavir: Use and Commercial Availability
Abacavir is an FDA-approved drug for treating HIV-1 infection. It is used in combination with other antiretroviral drugs, such as abacavir/lamivudine/zidovudine, abacavir/dolutegravir/lamivudine, and abacavir/lamivudine. Abacavir is categorized as a nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) and can be administered orally as a tablet or solution. The trade names of Abacavir include Epzicom (combination of Abacavir-Lamivudine), Triumeq (combination of Abacavir-Lamivudine-Dolutegravir), Trizivir (combination of Abacavir-Lamivudine-Zidovudine), and Ziagen.
Abacavir Structure and Mechanism of Action 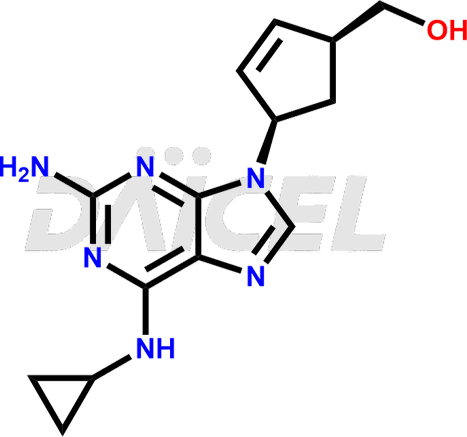
The chemical name of Abacavir is (1S,4R)-4-[2-Amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol. Its chemical formula is C14H18N6O, and its molecular weight is approximately 286.33 g/mol.
Abacavir is converted to its active metabolite, Carbovir triphosphate. It is an analog of deoxyguanosine-5¢-triphosphate (dGTP). It inhibits HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) activity.
Abacavir Impurities and Synthesis
Abacavir impurities may be categorized according to starting materials, reaction process, or degradation of the drug substance. The impurities formed may result from the synthetic process1, purification steps, or storage conditions. They can affect the drug’s quality, safety, and efficacy. Regular monitoring and analysis help ensure that the impurity levels remain within acceptable limits and do not pose a risk to patients.
Daicel provides a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for the Abacavir impurity standard, N6-Cyclopropyl-9H-Purin-2,6-diamine. The CoA is issued from a cGMP-compliant analytical facility and contains complete characterization data, such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity2. Additional characterization data, such as 13C-DEPT and CHN, can be provided upon request. Daicel can also prepare any unknown Abacavir impurity or degradation product. We give a complete characterization report on delivery.
References
- Daluge, Susan Mary, Therapeutic nucleosides, Wellcome Foundation Ltd., United Kingdom, US5034394A, July 23, 1991
- Veldkamp, A. I.; Sparidans, R. W.; Hoetelmans, R. M. W.; Beijnen, J. H., Quantitative determination of abacavir (1592U89), a novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, in human plasma using isocratic reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection, Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, Volume: 736, Issue: 1 + 2, Pages: 123-128, 1999
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the source of the Abacavir impurities?
The source of Abacavir Impurities may include raw materials, solvents, reagents, and degradation products formed during the manufacturing or storage of the drug product.
How are impurities in Abacavir detected and quantified?
Abacavir Impurities are detected and quantified using chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques, such as HPLC, UPLC, and LC-MS.
How are Abacavir impurities monitored?
Abacavir Impurities are monitored through regular testing of the drug substance and product during manufacturing and throughout its shelf-life.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Abacavir impurities?
Abacavir impurities are stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8 ⁰C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.


